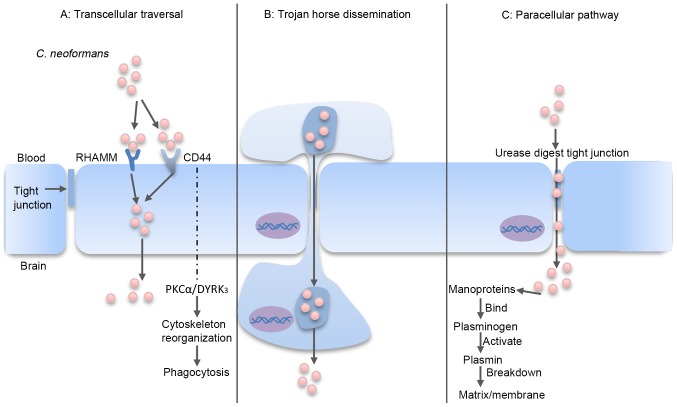
Figure 2.
C. neoformans traversal of the BBB. (A) Transcellular traversal: C. neoformans binds to receptors on the endothelial cell, which triggers cellular endocytosis (72–79). (B) Trojan horse dissemination: C. neoformans is phagocytosed by a macrophage, which is able to cross the BBB, resulting in pathogen transportation into the brain (85–92). (C) Paracellular pathway: C. neoformans damages and weakens the intercellular tight junctions, which facilitates passage of the organism between the endothelial cells (80–82). RHAMM, receptor of hyaluronan-mediated motility; CD44, cluster of differentiation 44; PKCα, protein kinase Cα; DYRK3, dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 3; BBB, blood-brain barrier; C. neoformans, Cryptococcus neoformans.