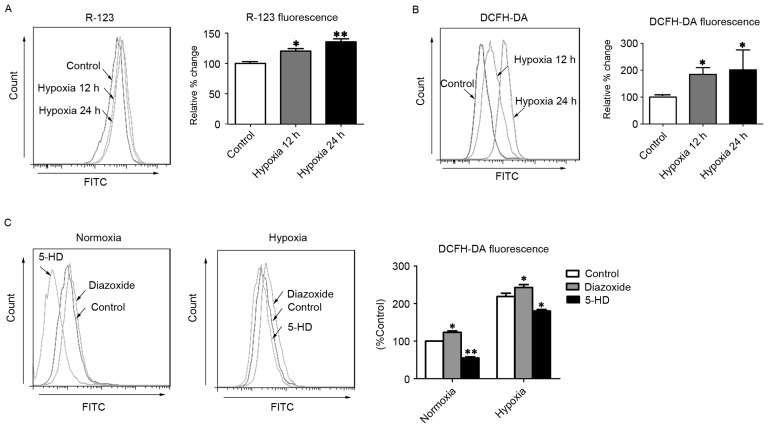
Figure 1.
MitoKATP channel opening increases intercellular ROS in hPASMCs. (A) The ΔΨm was assessed with R-123 fluorescence after cells were exposed to hypoxia for 12 or 24 h. (B) Levels of intracellular ROS were assessed by DCFH-DA fluorescence after cells were exposed to hypoxia for 12 or 24 h. (C) The intracellular ROS levels were assessed by DCFH-DA fluorescence after cells were treated with 5-HD or diazoxide upon normoxia or hypoxia. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. control. Data are expressed as percentage of control (n=3), and were analyzed by a Student's t-test. MitoKATP, mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channel; ROS, reactive oxygen species; hPASMCs, human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells; ΔΨm, mitochondrial membrane potential; R-123, rhodamine-123; DCFH-DA, 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate; 5-HD, 5-hydroxyde-canoate FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate.