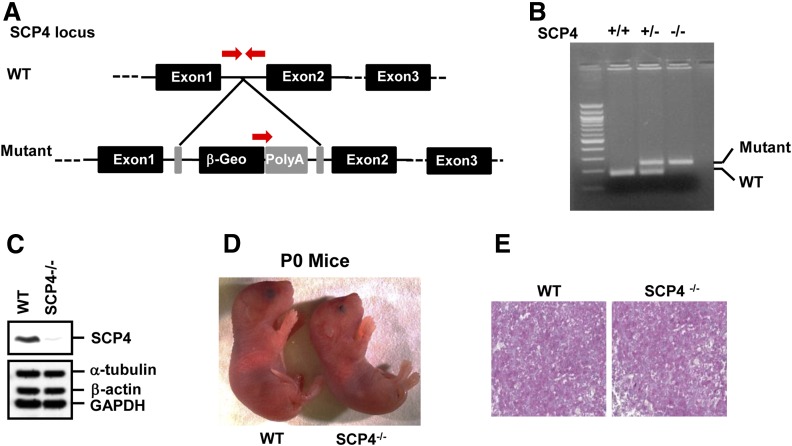
Figure 5.
Generation and characterization of SCP4 knockout mice. A: Generation of SCP4 knockout mice. Constructs of the WT allele and the disrupted allele are shown. Exons are represented by black boxes. Arrows represent the PCR primers used for genotyping. B: PCR genotyping of mouse tail DNA. Tail DNA was extracted from F2 littermates of heterozygote crosses and subjected to PCR using 5′ primers specific for the WT or knockout allele and a common 3′ primer as shown in A. C: SCP4 protein is undetectable in SCP−/− MEFs. MEF lysates isolated from E13.5 WT and SCP4−/− embryos were subjected to IB with indicated antibodies. D: Images of WT and SCP4−/− mice at birth (P0). SCP4−/− mouse was smaller than WT littermate (left). E: Liver glycogen storage is not affected by SCP4 gene deletion. The E18.5 liver sections of WT and SCP4−/− mice were stained with periodic acid Schiff to determine glycogen levels.