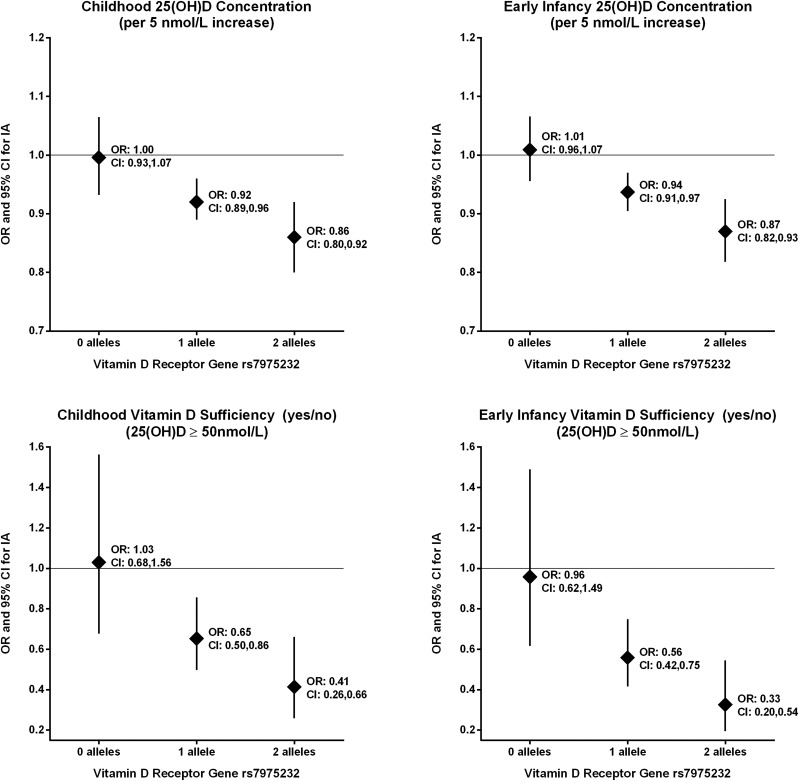
Figure 1.
ORs and 95% CIs for decreased risk of IA associated with 25(OH)D concentration (5 nmol/L increase) and being vitamin D sufficient (≥50 nmol/L) versus insufficient by number of minor alleles (the C allele) at rs7975232 in the vitamin D receptor gene. Analyses are adjusted for HLA-DR3/4 and the first two PCs indicating ancestry; and ORs are calculated from the SNP × vitamin D measure interaction terms. For childhood vitamin D measures, we analyzed 376 case subjects and their control subjects (297 case subjects with 3 control subjects, 71 case subjects with 2 control subjects, and 8 case subjects with 1 control subject) with complete plasma 25(OH)D and vitamin D genetic data. For the early infancy vitamin D measures, we analyzed 360 case subjects and their control subjects (269 case subjects with 3 control subjects, 83 case subjects with 2 control subjects, and 8 case subjects with 1 control subject).