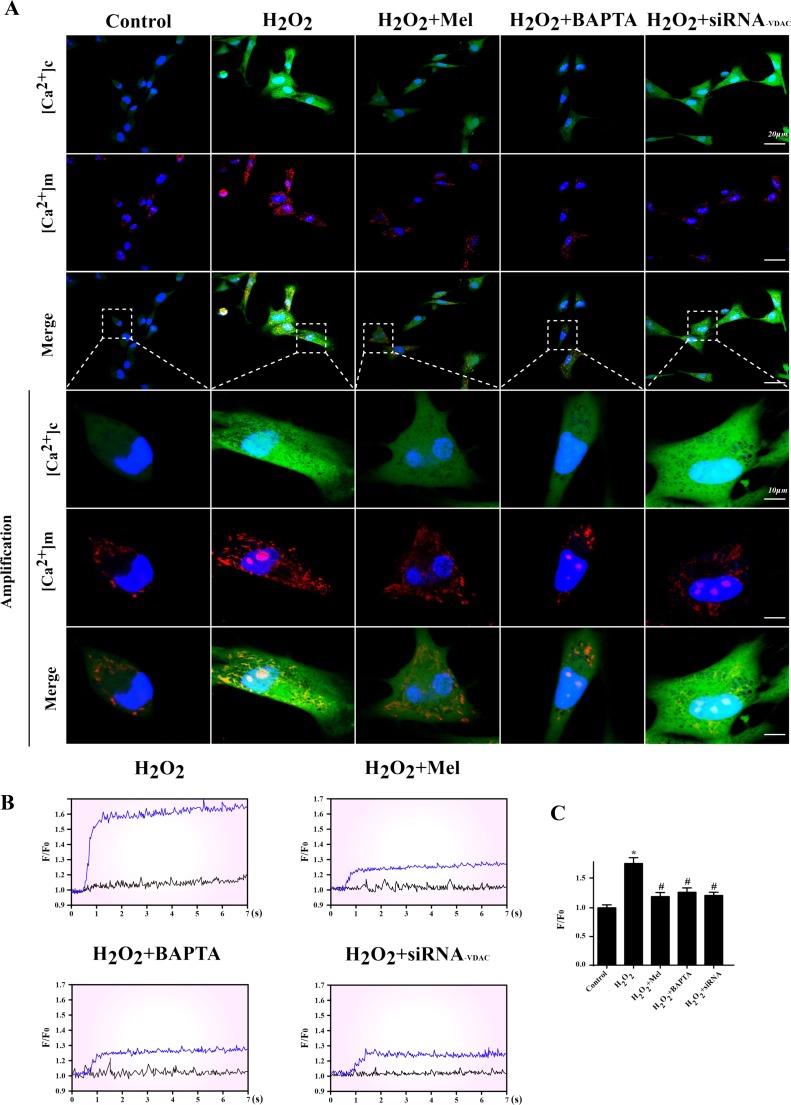
Fig. 5.
IP3R-dependent [Ca2+]c overload activated VDAC-mediated [Ca2+]m overload. a The co-immunofluorescence of [Ca2+]c and [Ca2+]m. Higher [Ca2+]c was associated with [Ca2+] through VDAC because siRNA knockdown of VDAC could significantly abate the increase in [Ca2+]m under oxidative stress. b, c The [Ca2+]m map via confocal microscopy by Rhod-2. Fluorescence intensity of Rhod-2 was measured by excitation wavelengths of 550 nm and emission wavelengths of 570 nm, respectively. Data (F/F0) were obtained by dividing fluorescence intensity (F) by (F0) at resting level (t = 0) which was normalized by control groups. *P < 0.05 vs. control group, #P < 0.05 vs. H2O2 group