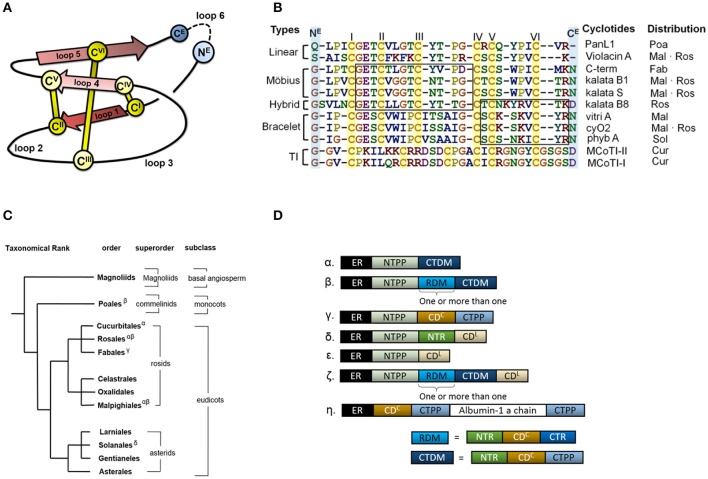
Figure 1.
Cyclotide sequence, structure and distribution. (A) Schematic representation of the structure of a cyclotide and the CCK framework. The cyclization point between the C- and N-termini (NE and CE, respectively) is highlighted, and the cysteine residues are labeled with Roman numerals. (B) Sequence alignment of representative cyclotides and their distribution in flowering plants. The cyclotides have been classified into five groups on the basis of their structural traits: Möbius cyclotides, bracelets, hybrids, linear cyclotides, and trypsin inhibitors (TI). Abbreviation code in plant orders: Poaceae (Poa), Malphigiales (Mal), Rosales (Ros), Fabales (Fab), Solanales (Sol) and Cucurbitales (Cur). The loops sharing sequence similarity are boxed. (C) Phylogeny of cyclotide-expressing flowering plants. To date, cyclotides have only been found in the eudicots. The family Violaceae belongs to the order of Malphigiales, Rubiaceae to Gentianales, and Cucurbitaceae to Cucurbitales. (D) Diversity of cyclotide precursor architectures. Precursor sequences consist of multiple domains: endoplasmic reticulum targeting signal (ER, black), N-terminal propeptide (NTPP, light blue), N-terminal repeat (NTR, green), cyclotide domain (CD), and C-terminal tail (CTR). Precursor architecture varies with both plant species and structural subfamily. Architecture types are labeled with Greek letters in (D), and their distribution is shown in (C). Oak1 (α) and Vok1 (β), precursors of kb1, are found in the Rubiaceae and Violaceae, respectively. Vok1 contains repeated domains. VocA (δ) and panitide pL1 (ε) are precursors of linear cyclotides and are found in the Violaceae and Poaceae, respectively. Precursors of these linear cyclotides do not contain a CTPP domain. TI subfamily precursors (ζ) contain both linear and cyclic cyclotides in the same sequence. Several architectures are often found in a single plant species. For example, Viola species contain VoK1 (α), VoC1 (β), and VocA (δ). In the precursor of Cter M, the cyclotide domain replaces the albumin-1b chain.