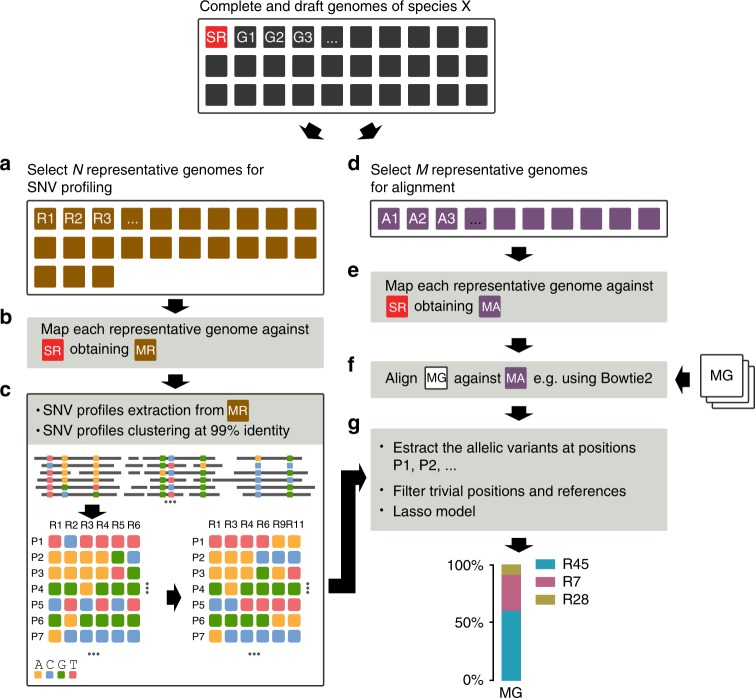
Fig. 1.
StrainEst overview. a Given the complete and the draft genomes of the species of interest (G1, G2,…) and the species representative (SR), the pairwise Mash distances are computed. Genomes with Mash distances >0.1 from the SR are discarded and the remaining ones are clustered to remove redundant sequences. For each cluster, the genome with the lowest average distance from the other members is chosen as a representative (R1, R2,…). b The representative sequences are mapped using nucmer against SR and ambiguous mappings are removed. c For each representative, the positions of the variant sites (P1, P2,…) are identified and the SNV profiles are extracted. The profiles are clustered at 99% identity to guarantee their representativeness. d To create a reference set for metagenomic reads alignments that takes into account the variability of the species, representative genomes are selected for the metagenome alignment step (A1, A2, …) and (e) mapped against SR. f For each metagenome (MG), the reads are aligned to the chosen genomes using Bowtie 2. g The frequencies of the allelic variants at the variant positions defined in step (c) are extracted from the BAM file; sites with low coverage are filtered according to user-defined filtering parameters; the relative abundance profile is finally inferred by Lasso regression