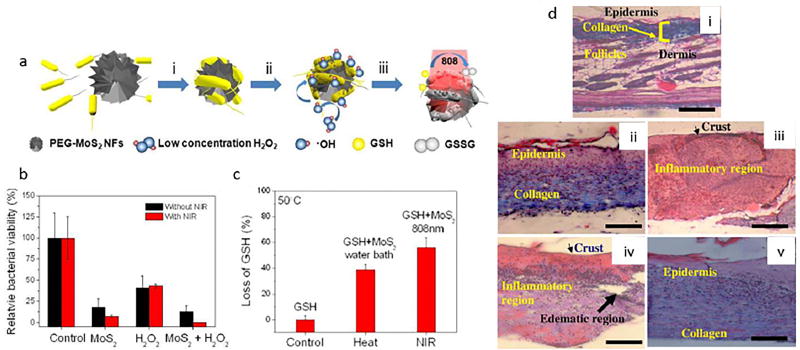
Figure 11.
a) Scheme of a PEG-MoS2 nanoplatform to destroy bacteria via a synergistic combination of peroxidase catalysis and photothermal activation: (i) Capture of the nanoplatform by bacteria; (ii) catalytic activity of the nanoplatform decomposes low-concentration H2O2, leading to generation of ·OH that damages cell wall integrity; 808 nm laser treatment induces hyperthermia, causing accelerated GSH oxidation, b) Relative bacterial viability for B. subtilis, obtained after incubation with PBS, MoS2 (100 µg mL−1), H2O2 (100 µM), or MoS2+H2O2 for 20 min, with or without the laser treatment, c) GSH loss after heating by water bath or 808 nm NIR-irradiation compared to control (non-treated GSH) for 20 min at 50 °C. Reprinted with permission from ref. [315], copyright 2016, American Chemical Society, d) Photomicrographs indicating PDT-triggered healing: (i) normal skin, (ii) wound without infection, (iii) infected wounds, (iv) infected wounds with 200 µM pl–cp6 treatment, and (v) infected wounds with 200 µM pl–cp6 treatment plus with exposure to the light dose of 60 J/cm2. Reprinted with permission from ref. [316], copyright 2013, Springer.