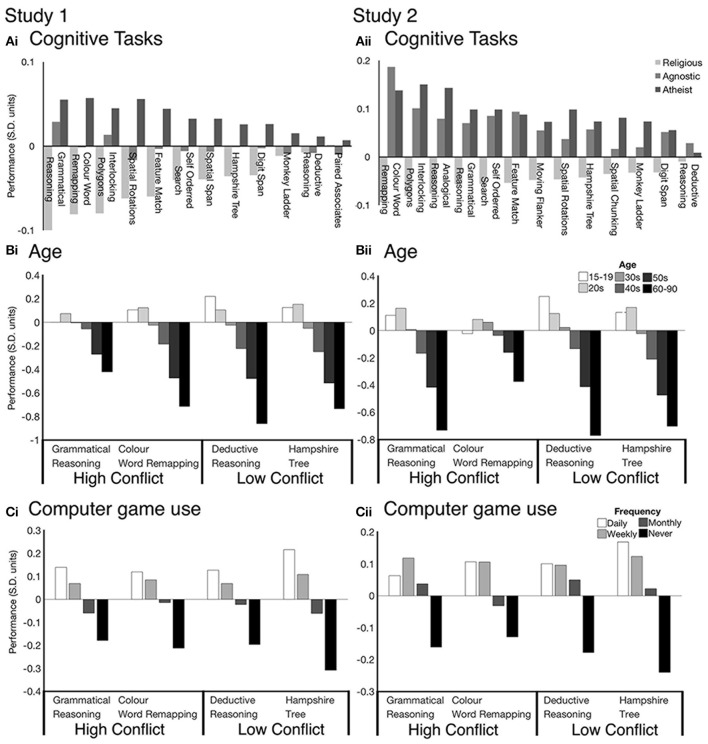
Figure 3.
The non-religious groups consistently outperforms the religious group across cognitive tasks in both studies 1 and 2 (Ai,Aii). The largest group effects are seen during cognitive tasks with conflict between intuitive and logical processes (Religious, light gray; Agnostic, gray; Atheist, dark gray). We demonstrate that these effects are specific to religiosity by comparing tasks with high and low cognitive conlfict against alternate demographic variables Age (Bi,Bii) and Computer game use (Ci,Cii). Performance scores for all cognitive tasks are in Standard Deviation units (Mean = 0, SD = 1).