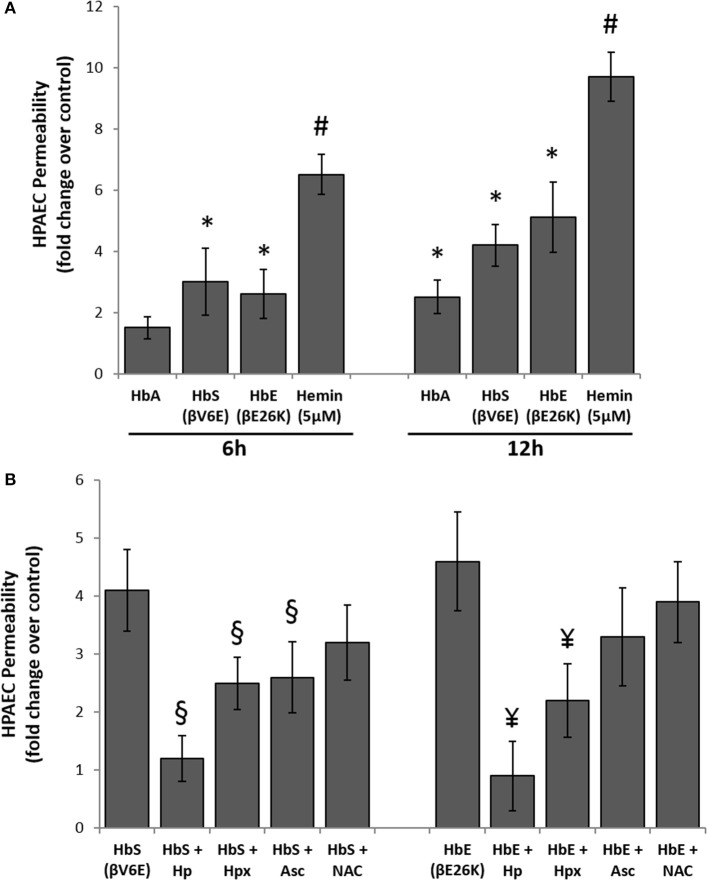
Figure 3.
Cell free hemoglobin variants causes disruption of pulmonary endothelial monolayer. (A) HPAEC monolayer were grown on Transwell inserts and then exposed to ferrous forms of HbA or HbS or HbE at equimolar concentration (100 μM) either for 6 or 12 h in the presence of FITC conjugated dextran, 40 KD. Endothelial monolayer integrity was assessed by measuring the passage of FITC-dextran molecule through monolayer. FITC-green fluorescence was monitored by fluorescence plate reader as described in the methods section. Values are presented as average fold difference over control (N = 3). (B) In a similar set of experiments HPAEC were exposed to either HbS (100 μM) or HbE (100 μM) with or without equimolar of either Hp, Hpx or Asc or NAC for 12 h in the presence of FITC conjugated dextran. Endothelial monolayer integrity was assessed as mentioned before by measuring FITC-dextran fluorescence in the bottom chamber (N = 3). Values obtained from different treatment groups were compared using Mann-Whitney U-test. *P < 0.05 vs. untreated control, #P < 0.001 vs. untreated control, §P < 0.05 vs. HbS, ¥P < 0.05 vs. HbE.