Figure 2.
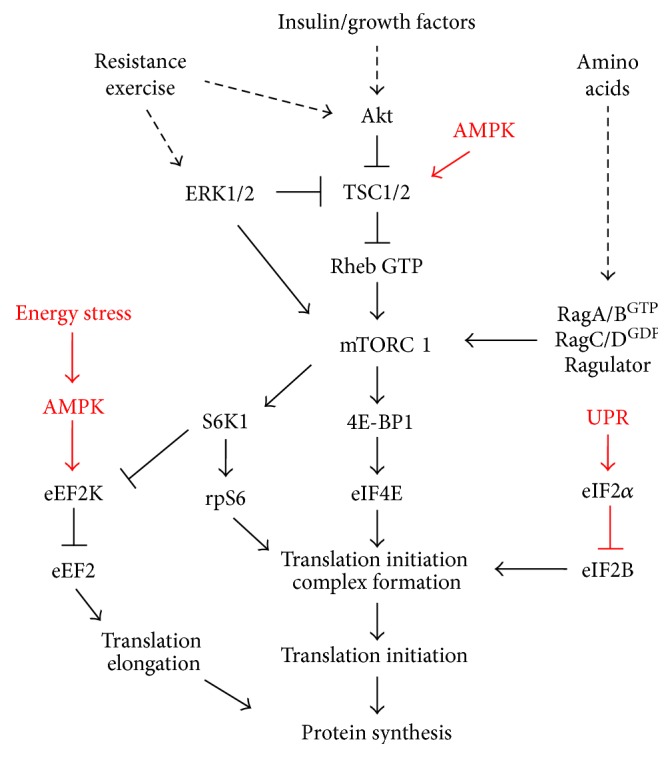
mTORC1 signaling regulation by acute anabolic stimuli. Exercise, growth factors, and nutrients can positively regulate muscle mTORC1 signaling. Cancer cachexia can suppress mTORC1 signaling through disrupted oxidative capacity and mitochondrial quality control. Disrupted muscle homeostasis can promote energy stress and an unfolded protein response, which negatively regulate mTORC1 signaling at several levels. Black lines: positive regulation. Red lines: negative regulation. ERK, extracellular signal-related kinases; Akt, protein kinase B; TSC1/2, tuberous sclerosis complex 1 and 2; Rheb, ras homolog enriched in brain; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; RagA/B, RagA and RagB heterodimer; RagC/D, RagC and RagD heterodimer; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; S6K1, ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1; S6, ribosomal protein S6; 4E-BP1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor binding protein 1; eIF4E, eukaryotic initiation factor 4E; eEF2K, eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase; eEF2, eukaryotic elongation factor 2; eIF2α, eukaryotic initiation factor alpha; eIF2B, eukaryotic initiation factor 2B; UPR, unfolded protein response.
