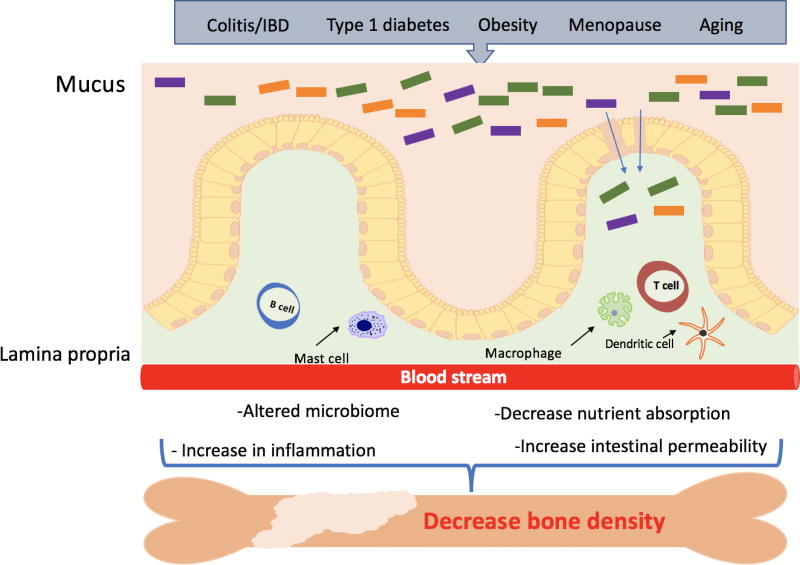
Figure 3. Model of intestinal epithelial disruption signals that can regulate bone density.
Many factors such as aging, menopause and metabolic diseases are known to disrupt the intestinal epithelial layer. They can modulate gut microbiota composition and activity, increase intestinal permeability, inflammation and decrease nutrient absorption. These changes can result in local and systemic responses that can affect bone density.