Fig. 4.
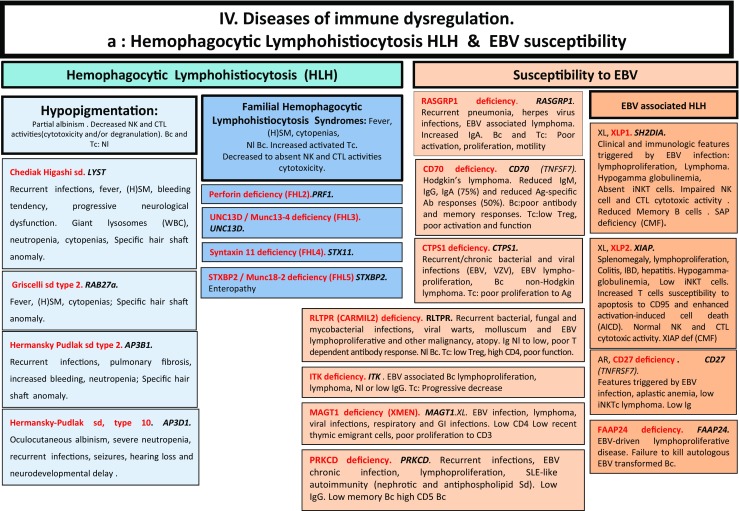
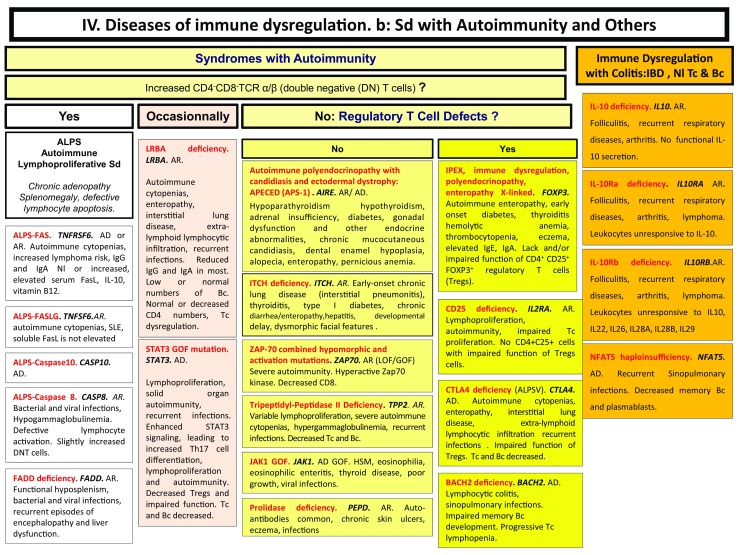
Diseases of immune dysregulation. a Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. b Other diseases of immune dysregulation. Ab: antibody; AD: autosomal dominant transmission; Ag: antigen; ALPS: autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome; APS: autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome; AR: autosomal recessive transmission; Bc: B cells; CD: cluster of differentiation; CMF: flow cytometry; CTL: cytotoxic T lymphocytes; def: deficiency; DNT: double negative T cells; EBV: Epstein Barr virus; FHL: familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; GOF: gain-of-function; HLH: hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; (H)SM: (hepato)splenomegalia; IBD: inflammatory bowel disease; Ig: immunoglobulin; IL-10: interleukin-10; LOF: loss-of-function; iNKT: invariant NKT cells; NK: natural killer cells; Nl: normal; sd: syndrome; SLE: systemic lupus erythematous disease; Tc: T cells; TCR: T cell receptor; XL: X-linked transmission
