FIGURE 1.
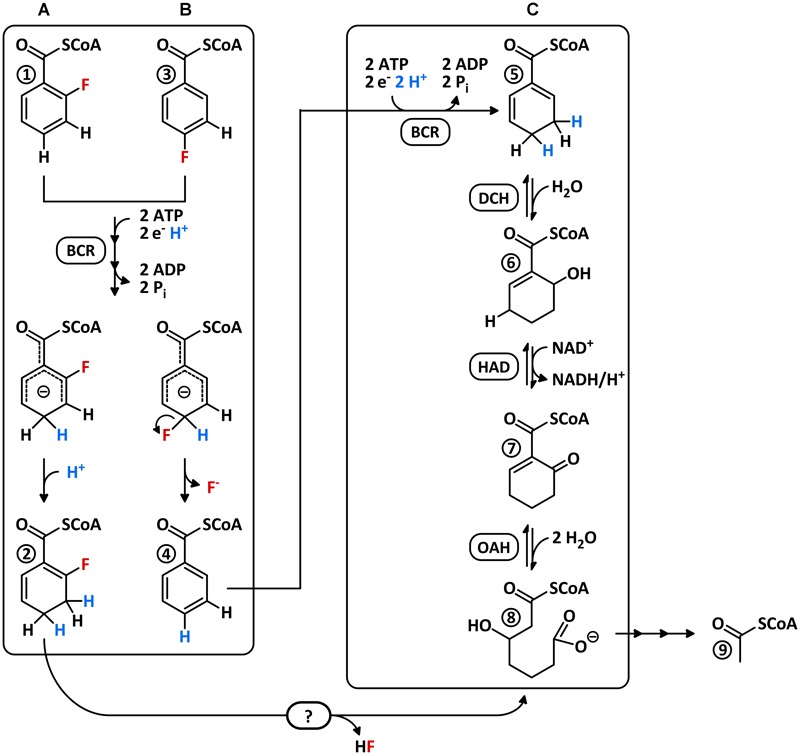
Scenarios for the catabolism of 2- and 4-F-BzCoA via the BzCoA degradation pathway. Putative conversion of (A) 2-F-BzCoA to F-1,5-dienoyl-CoA and (B) experimentally verified defluorination 4-F-BzCoA to BzCoA by class I BCR. Both compounds are suggested to be ATP-dependently reduced to a common anionic transition state, which is either protonated at C3/C5 to a 2- or 6-F-1,5-dienoyl-CoA (A) (only the 2-F-isomer is shown) or defluorinated to BzCoA (B) at the para-position. Direct defluorination of 2-F-BzCoA by BCR is unlikely as it would require protonation at C2 instead of C4. (C) BzCoA degradation pathway involving ATP-dependent BCR, DCH, HAD, and OAH. At the beginning of this study it was unknown how 2-F-BzCoA is channeled into the BzCoA degradation pathway.
