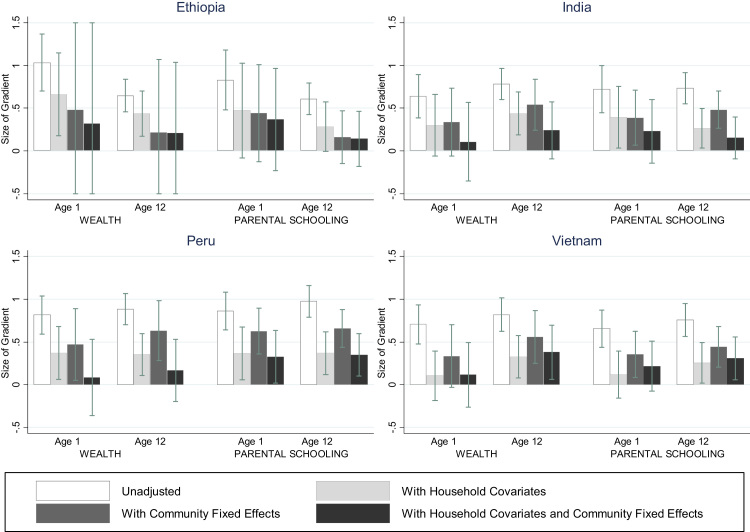
Fig. A5.
Disparities in HAZ from wealth and parental schooling at ages 1 and 12 y, with and without controls for household variables and community fixed effects, Young Lives study. Household covariates are mother’s height in centimeters, mother’s age in years, ethnicity indicator variables, and an indicator variable for the mother speaking the region’s official language. The variable not defining the disparitiy is also included: the parental schooling index is included as a household covariate in the adjusted disparities from wealth and vice versa.). Community fixed effects are defined by location at age 1y. Confidence intervals are wide for community fixed effects in Ethiopia for the wealth disparity because 14 of 20 communities do not contain households in both top and bottom quartile. Confidence intervals for Ethiopian wealth disparities adjusted for community fixed effects and mother characteristics (height, age, ethnicity, and language) with community fixed effects are truncated at −10 for height and vocabulary and are truncated at −0.5 and 1.5. HAZ is standardized according to World Health Organization Growth Standards/References (de Onis et al., 2007; World Health Organization, 2006).