Figure 7.
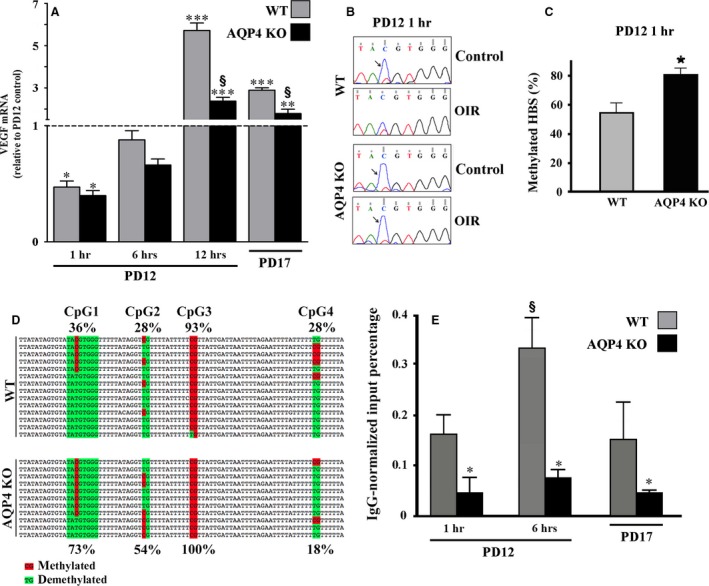
Analysis of VEGF mRNA levels, CpG methylation status and physical interaction between HIF‐1α and HBS. (A) VEGF mRNA levels were evaluated by qPCR at different times after hypoxia. At 1 hr, hypoxic levels of VEGF mRNA were significantly lower than in normoxia to then increase at 6 hrs with a peak at 12 hrs followed by a drastic reduction at PD17. The absence of AQP4 reduced VEGF mRNA levels already after 12 hrs of hypoxia. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus respective control; § P < 0.001 versus WT; anova). (B) Representative chromatograms of PCR bisulphite sequencing and relative C/T double peaks in the CpG sites of the HBS. Blue peaks (5 methyl CpG, arrows) indicate that in normoxic controls, the CpG site was methylated in retinas of both WT and AQP4 KO mice, while in OIR, the CpG site became demethylated in WT, but not in AQP4 KO mice. (C) The COBRA analysis confirmed that the methylation frequency of the CpG site in the HBS was significantly higher in AQP4 KO than in WT mice (*P < 0.05 versus WT, unpaired Student's t‐test). (D) The cloning and the sequencing of bisulphite‐treated DNA relative to four CpG sites (CpG1‐4) showed that the methylation frequency of the CpG1 site in the HBS was about twofold higher in AQP4 KO than in WT mice, similarly for CpG2. CpG3 was completely methylated while CpG4 was strongly demethylated, both in a similar fashion between WT and AQP4 KO mice. (E) HIF‐1α chromatin immunoprecipitation and HBS‐specific qPCR (ChIP‐qPCR) were performed on WT and AQP4 KO mice. In WT mice, the physical interaction between HIF‐1α and the HBS starts quickly and reaches a peak after 6 hrs, while in AQP4 KO mice, the interaction is always very low and appears to be insensitive to hypoxia (*P < 0.05 versus relative WT; § P < 0.05 6 hrs versus 1 hr and 6 hrs versus PD17 in WT, anova).
