Figure 1.
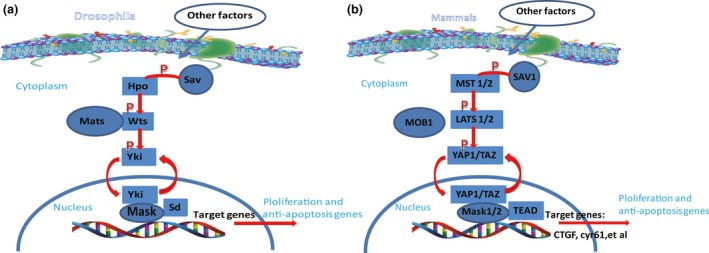
The Hippo signalling pathway in Drosophila and mammals. (A) The Drosophila Hippo pathway. In Drosophila, when Yki is relieved from inhibition through phosphorylation‐dependent or phosphorylation‐independent mechanisms, its nuclear translocation then drives target gene expression to regulate cellular proliferation and apoptosis. The phosphorylation mechanism depends on the core kinase cascade including Hpo, Wts, Sav and Mats. (B) The mammalian Hippo pathway. In mammals, YAP1 and TAZ localize to the nucleus to interact with TEAD, driving target gene expression to regulate cellular proliferation and apoptosis. After phosphorylation, MST1/2 in turn phosphorylates LATS1/2, facilitated by scaffold proteins SAV1 and MOB1. MOB1 also phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2. Activated LATS1/2 phosphorylate YAP1 and TAZ. YAP1 interacts with Mask1/2 to form complex.
