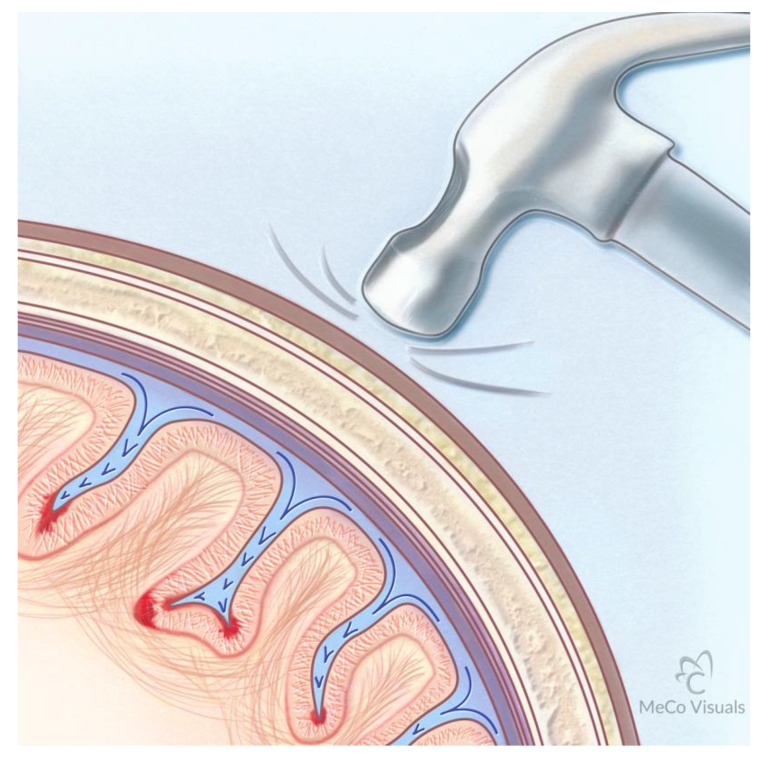
Figure 5.
Water Hammer Illustration of the mechanism whereby traumatic impact to the skull results in transmission of force to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). As the elastic brain impacts the non-compressible calvarium, the non-compressible CSF is driven into the sulci. The base of the sulcus receives the major force of the CSF impulse. The alignment of the axons in the gray matter at the base of the sulcus is oriented parallel to the vector force while the U fiber bundles at the base are oriented perpendicular to the vector. Differing rigidity features of the gray and white matter result in shearing at that interface. The areas of red intensity at the base of the sulci represent sites of major force dissipation. The intense linear red at the interface between the gray matter and the U fiber bundles represents areas of bleeds from vascular injury.