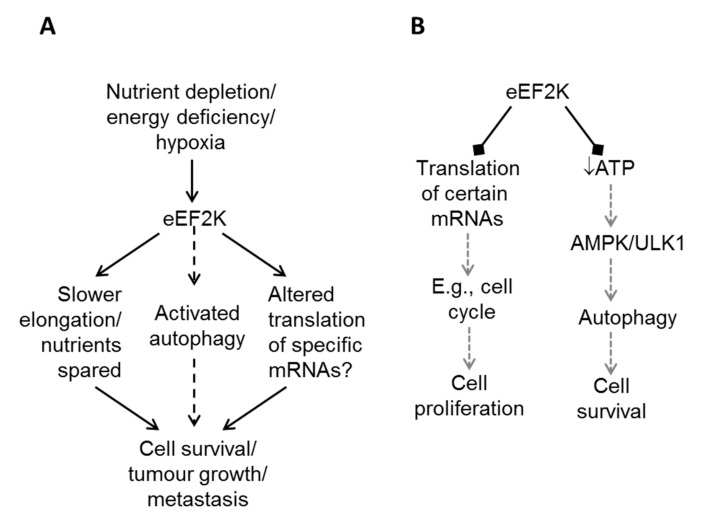
Figure 2.
Roles of eEF2K in cancer cells. (A) In many types of tumour cells, and likely in more advanced solid tumours, eEF2K helps protect cells against nutrient depletion and other stresses by slowing down protein synthesis (thereby conserving resources) and/or altering the translation rates of specific mRNAs and thus the levels of the corresponding proteins. Some studies also suggest that eEF2K can promote autophagy, but this is not a general effect (dashed line). (B) eEF2K may also restrain tumour initiation, e.g., in colorectal cancer, by inhibiting general protein synthesis and/or the translation of specific mRNAs. Also, by maintaining ATP levels (through inhibition of protein synthesis), eEF2K may also indirectly inhibit the activation of autophagy.