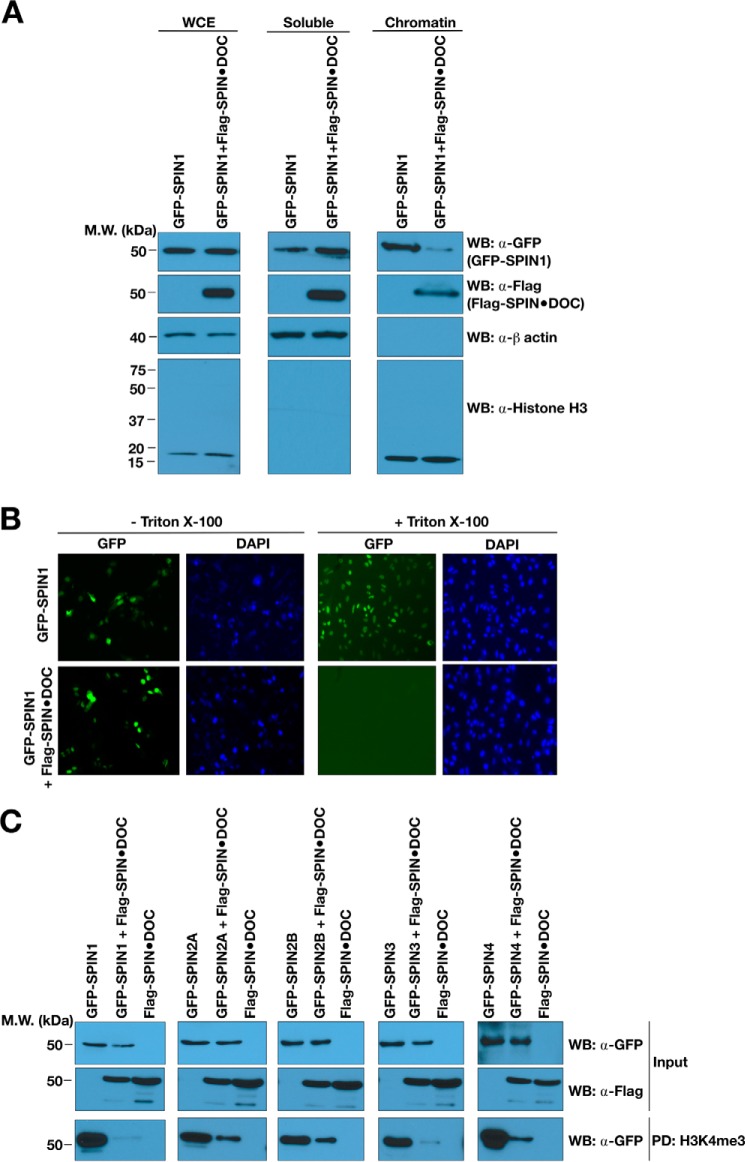
Figure 3.
SPIN·DOC disrupts SPIN1 binding to chromatin in cells. A, GFP-SPIN1 and FLAG-SPIN·DOC were transfected or co-transfected into HeLa cells, and cell lysates were biochemically separated into soluble and chromatin-enriched fractions that were then analyzed by Western blotting (WB) with the indicated antibodies. Whole-cell extract (WCE) is shown to control for total GFP-SPIN1 and FLAG-SPIN·DOC. Histone H3 and β-actin levels are shown as controls for the integrity of the fractionation. MW, molecular weight. B, GFP-SPIN1 and FLAG-SPIN·DOC were transfected or co-transfected into HeLa cells. Shown is a representative image of GFP localization determined in cells with or without Triton X-100 treatment prior to fixation and visualization by fluorescence microscopy. DAPI staining is shown to indicate the nuclei of cells. C, HEK293T cells were transfected or co-transfected with SPIN·DOC and the GFP-SPIN family (SPIN1, 2A, 2B, 3, and 4). The whole-cell lysates were then subjected to pulldown analysis with biotinylated H3K4me3 peptides. The pulldowns were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis using α-GFP antibodies.