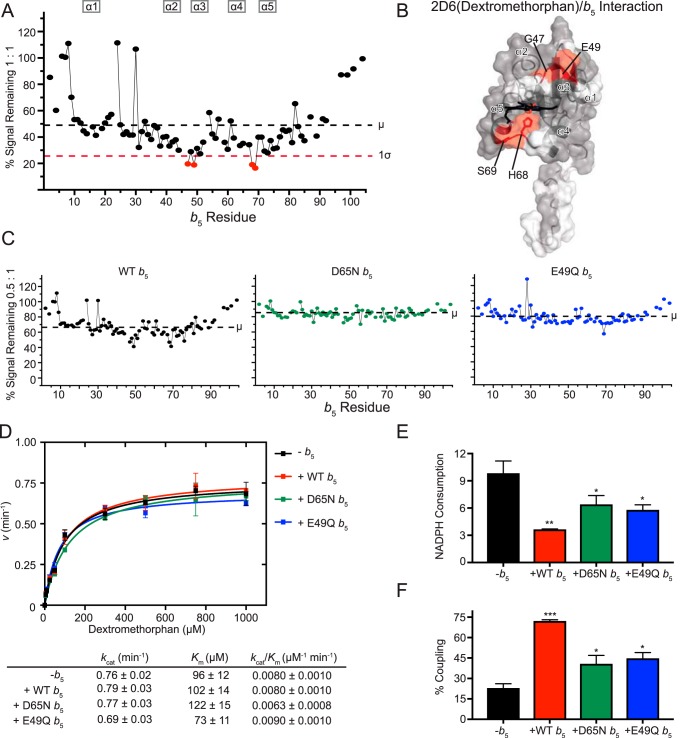
Figure 5.
Interaction of CYP2D6(dextromethorphan) with [15N]b5 as determined by NMR and catalytic modulation of b5 on CYP2D6-mediated metabolism of dextromethorphan. A, b5 resonance intensity plot at a 1:1 (CYP2D6(DXM):[15N]b5) ratio normalized to the free b5 resonance intensity. The color code is as described in the legend to Fig. 2B. B, human soluble domain b5 structure (PDB entry 2I96) with residues displaying differential broadening effects colored red, residues that are assigned in the NMR spectrum colored gray, and unassigned residues colored white. C, b5 resonance intensity plots comparing the effects of line broadening between WT b5 and b5 mutants D65N and E49Q at a fixed 0.5:1 (CYP2D6(DXM):[15N]b5) ratio. D, effect of WT b5 and mutants on Michaelis–Menten kinetic parameters of CYP2D6-mediated O-demethylation of dextromethorphan. Each sample was generated in triplicate with S.D. illustrated by error bars. Steady-state kinetic constants below are shown with S.D. E, measurement of NADPH consumed (nmol of NADPH/min/nmol of CYP2D6) for CYP2D6 dextromethorphan reaction at a fixed dextromethorphan concentration of 1 mm. Samples were generated in duplicate with the S.D. illustrated by error bars. F, percent coupling of CYP2D6-mediated O-demethylation of dextromethorphan. Samples were generated in duplicate with the S.D. illustrated by error bars. *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001.