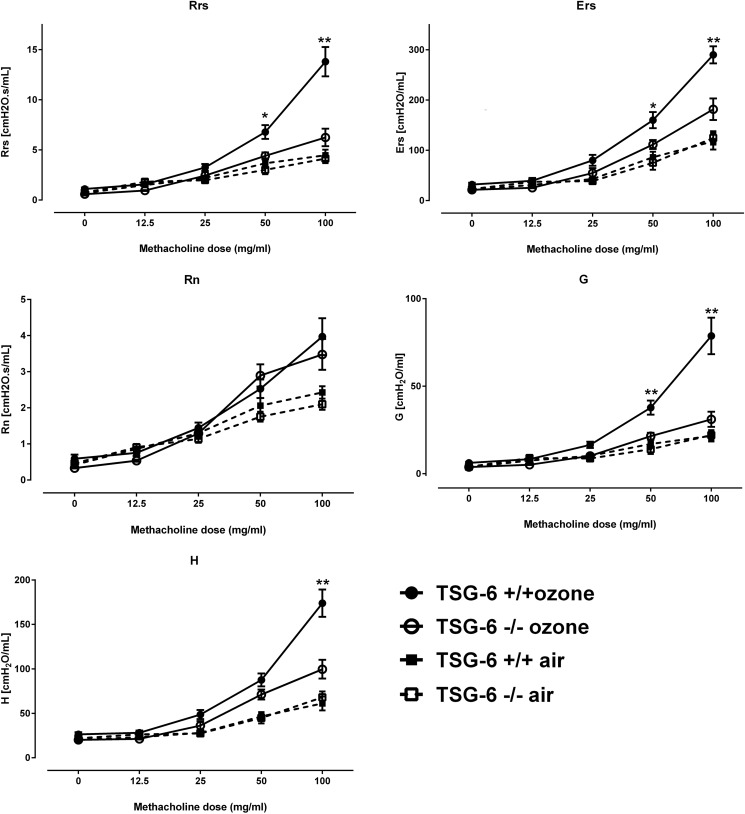
Figure 3.
Increased airway resistance and stiffness in TSG-6–sufficient mice after ozone exposure, which is due to increases in peripheral tissue values. Mice were exposed to 2 ppm ozone for 3 h, and 24 h later, they were anesthetized, paralyzed, tracheotomized, intubated, and phenotyped for airway physiology measurements via flexiVent. Rrs, respiratory system (whole-lung) resistance; Ers, respiratory system (whole-lung) elastance; Rn, Newtonian (large-airway) resistance; G, damping (peripheral lung resistance); H, peripheral lung elastance. Results are represented as means ± S.E. (error bars) of measurements. The experiment was repeated twice. n = 8/group. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 t test with Holm–Sidak correction for multiple testing.