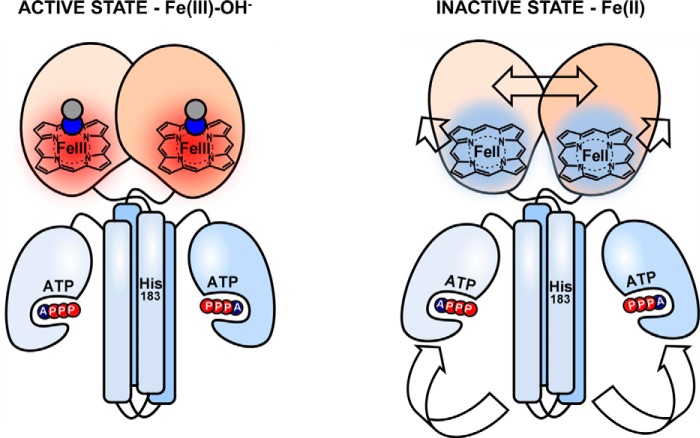
Figure 9.
Proposed intramolecular signal transduction mechanism in the full-length AfGcHK protein that explains its catalytic inactivation upon heme reduction. Heme reduction induces conformational changes in the globin domain, simultaneously widening and splitting its internal dimeric interface, and making the initial residues of H7 accessible to the solvent. This signal is propagated down to the kinase domain via the linker, causing the ATP binding site to be separated from His183, hindering the autophosphorylation of the latter residue. Data previously obtained by our group indicated that heme reduction increases the enzyme's KmATP value and thus reduces the ATP affinity of the kinase domain (8).