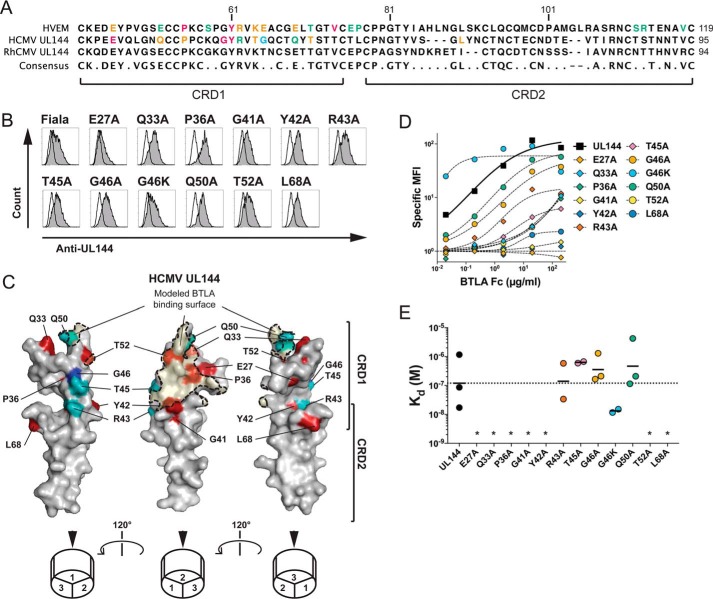
Figure 1.
Modeling BTLA binding epitope in ligand selective CMV UL144. A, the extracellular domains of human HVEM and human CMV UL144 were aligned to show the positions of residues mutated in UL144 here and in HVEM from previous studies (10, 20). B, 293T cells transduced with wild-type or mutated human CMV UL144 were stained with anti-UL144 (clone 2F11). Histograms show UL144 expression (gray) overlaid onto cells transfected with control vector. C, three images of human CMV UL144 rotated 120° about the y axis showing mutated surface residues. Structure was predicted using HVEM as a model and with residue dihedral angles φ and ψ conforming to allowed ranges within the Ramachandran plot. Human CMV UL144 surface is shown in gray with CRD1 and CRD2 indicated. Residues required for BTLA binding are colored as follows: Glu27, Gln33, Pro36, Gly41, Tyr42, Thr52, and Leu68 in red (required) and Arg43, Thr45, and Gln50 in teal (no significant effect). Gly46 in blue showed increased binding when mutated to Lys. The BTLA binding surface was predicted using the structure of HVEM and BTLA together and shaded in orange. D and E, 293T cells transduced with wild-type or mutated human CMV UL144 (group C strain) were stained with the indicated concentrations of BTLA-Fc. Graphs in D show binding curves for the indicated UL144 mutants from a representative experiment. Kd of BTLA-Fc binding to UL144 proteins were plotted in E (geometric mean, at least three experiments per mutation). *, not determined.