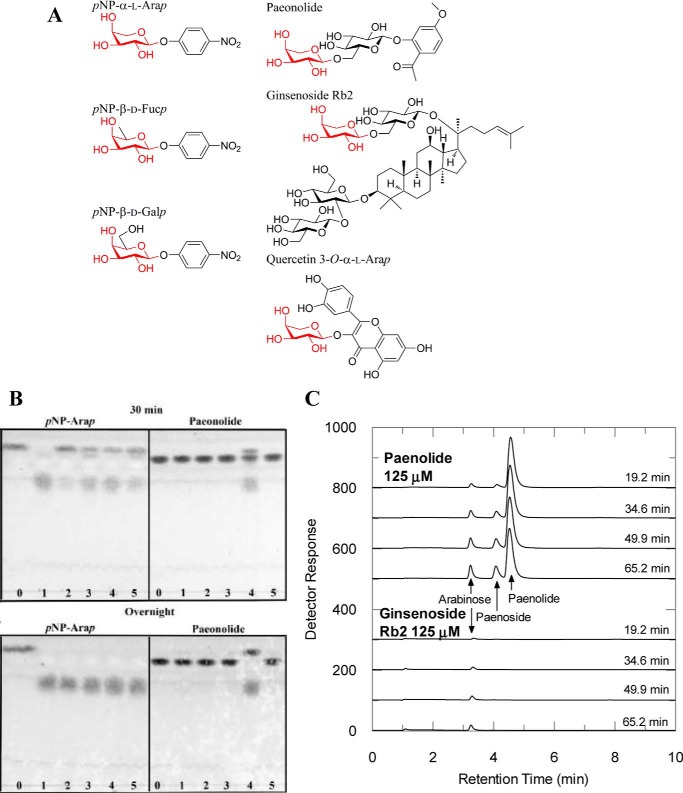
Figure 1.
A, chemical structures of substrates; B, TLC analysis on the hydrolysis of pNP-α-l-Arap and paeonolide by BlArap42B and other GH42 enzymes; and C, HPAEC-PAD analysis on the hydrolysis of plant glycosides containing a non-reducing end α-l-arabinopyranoside by BlArap42B. A, structures of pNP-α-l-Arap, pNP-β-d-Fucp, pNP-β-d-Galp, paeonolide, ginsenoside Rb2, and quercetin 3-O-α-l-Arap are shown. pNP-α-l-Arap and pNP-β-d-Fucp differ from pNP-β-d-Galp by lacking C6 and C6-OH, respectively. Non-reducing end α-l-arabinopyranose is found in 2-acetyl-5-methoxyphenyl-α-l-Arap-(1,6)-β-d-Glcp (paeonolide) from Paeonia, ginsenoside Rb2 from P. ginseng, and quercetin 3-O-α-l-Arap from P. guajava Linn. B, substrate activity screening using TLC of BlArap42B (lane 4) and previously characterized bifidobacterial GH42 β-galactosidases, Bga42A (lane 1), Bga42B (lane 2), and Bga42C (lane 3) from B. longum subsp. Infantis, ATCC 15697 as well as BlGal42A (lane 5) from B. animalis subsp. lactis Bl-04 (lane 0) are controls without enzyme. BlArap42B (land 4) displayed significant activity toward paeonolide by 30 min incubation, with complete hydrolysis overnight. Bga42A, Bga42B, Bga42C, and BlGal42A did not show significant activity toward paeonolide after 24 h incubation, despite their ability to hydrolyze pNP-α-l-Arap. C, HPAEC-PAD chromatograms showing activity toward paeonolide and ginsenoside Rb2. Paeonoside is the de-arabinosylated product of paeonolide. Activity was not detected toward quercetin 3-O-α-l-Arap. Peaks corresponding to the substrate ginsenoside Rb2 and its de-arabinosylated product (= ginsenoside Rd) could not be detected in the elution range under the conditions employed (see “Experimental procedures”).