Figure 3.
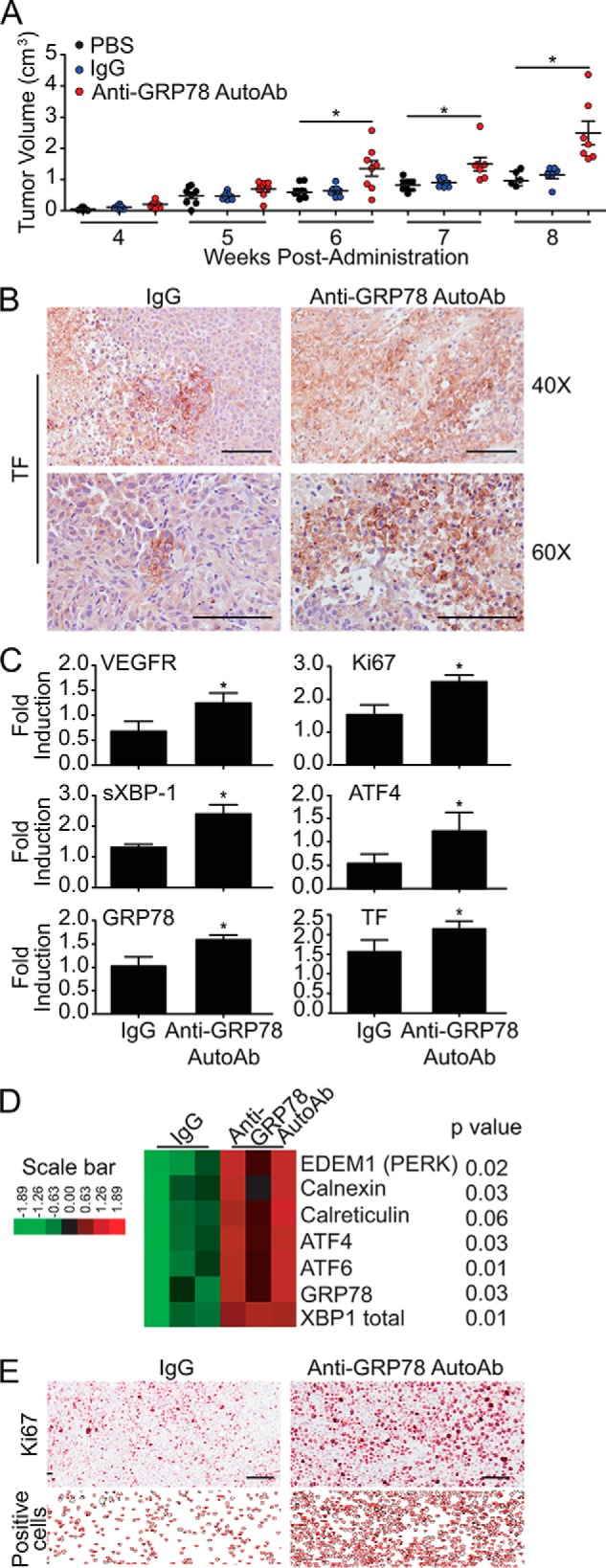
Anti-GRP78 AutoAbs accelerate tumor growth in mice and increase protein expression of TF and UPR markers. A, treatment of NOD/SCID mice bearing DU145 xenografts with anti-GRP78 AutoAbs (60 μg/ml) significantly increases tumor growth compared with PBS-treated or human IgG-treated (60 μg/ml) mice (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001 versus IgG and PBS treatment; n = 8/group). Mean tumor volume ± S.E. (error bars) is shown. B, IHC analysis of tumors from mice treated with anti-GRP78 AutoAbs demonstrates an increase in TF expression compared with human IgG treatment. Scale bar, 100 μm. C, quantitative real-time PCR analysis of tumors from mice treated with anti-GRP78 AutoAbs demonstrates increased mRNA expression of TF, VEGR, Ki67, spliced XBP1, ATF4, and GRP78 (*, p < 0.05 versus IgG treatment; n = 3). D, gene expression levels of seven UPR markers (derived by NanoString®) following treatment with control human IgG (60 μg/ml) or anti-GRP78 AutoAbs (60 μg/ml). p values are indicated for each gene (n = 3/treatment). E, IHC analysis of the proliferation marker Ki67 demonstrates an increase in positive cells in the anti-GRP78 AutoAb-treated group compared with control human IgG. Representative images of five sections are shown. ImageJ was used to count the number of Ki67-positive cells. Scale bar, 100 μm.
