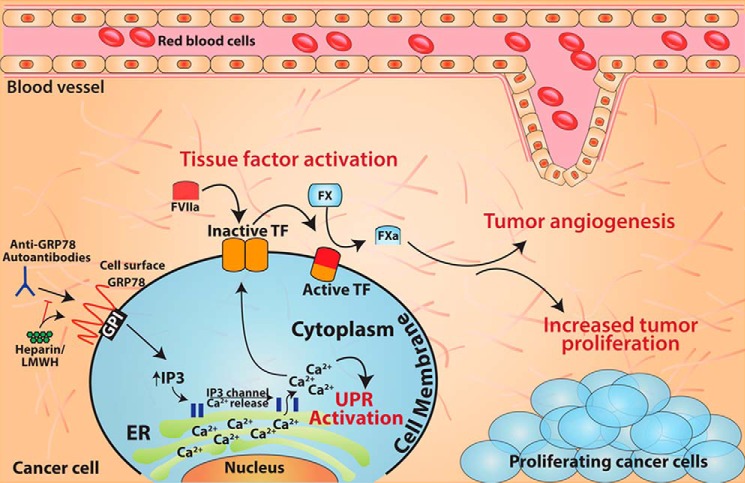
Figure 6.
Summary model. Anti-GRP78 AutoAbs increase tumor growth by binding to cell-surface GRP78 and activating TF. This interaction can be interrupted by treatment with heparin or enoxaparin. Binding of anti-GRP78 AutoAbs to cell-surface GRP78 induces elevated cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations that can activate the pro-survival UPR pathway and increase TF activity. Overall, this interaction leads to an increased rate of tumor growth, improved angiogenesis, and, potentially, enhanced survival via UPR activation.