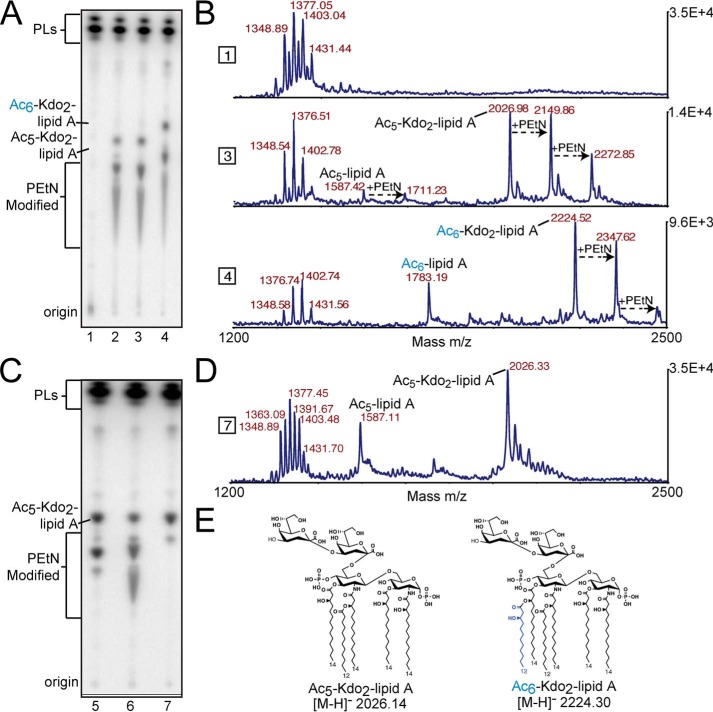
Figure 3.
TLC and MALDI-MS structural analysis of biosynthetically engineered deep-rough E. coli that produce minimal Kdo-lipid A domains. Text labels along the plate depict origin where lipid material was spotted before TLC separation, as well as proposed lipid species. A, each lane represents lipid material from E. coli K12 W3110 ΔlpxMΔlpxT (lane 1), ΔlpxMΔlpxTΔrfaDFC (lane 2), ΔlpxMΔlpxTΔrfaDFC harboring pQlink (lane 3), or pQlink::LpxN (lane 4). B, MALDI-MS analysis of non-radiolabeled material in corresponding lanes in A. Right y axis denotes total counts, and the x axis is of the m/z range analyzed. C, each lane represents lipid material isolated from E. coli K12 W3110 ΔlpxMΔlpxTΔrfaDFCΔeptA (lane 5), ΔlpxMΔlpxTΔrfaDFCΔeptB (lane 6), or ΔlpxMΔlpxTΔrfaDFCΔeptAΔeptB (lane 7). D, MALDI-MS analysis of non-radiolabeled material in corresponding lanes in C. Right y axis denotes total counts, and the x axis is of the m/z range analyzed. E, major structures of penta-acylated or LpxN modified Kdo2-lipid A species in synthetically engineered E. coli. Other important structures can be found in supplemental Fig. S3.