Figure 1. ASF1a is required for NHEJ and resistance to DSBs.
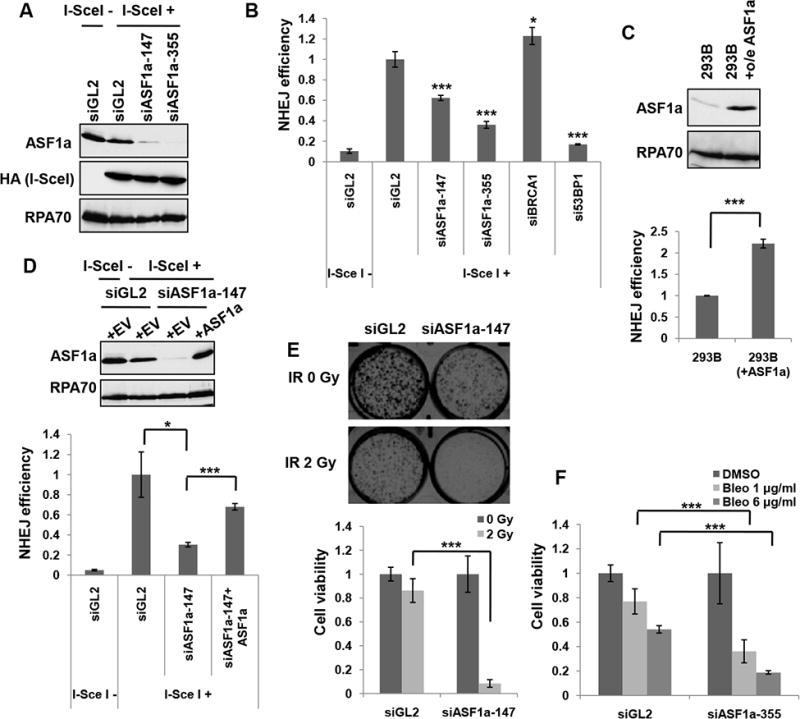
(A) Immunoblots of the NHEJ/DsRed293B lysates transfected with two different ASF1a targeting siRNAs, 48 hr after transfection of HA-I-SceI plasmids. HA-I-SceI was detected by anti-HA antibody. (B) ASF1a knockdown reduces NHEJ efficiency. NHEJ efficiency is measured as described in the METHOD DETAILS and represented as mean ± S.D. of triplicates. ***, P< 0.005; *, P< 0.05. (C) ASF1a overexpression increases NHEJ efficiency. 293B having stable overexpression (o/e) of ASF1a was compared with wild-type 293B for ASF1a expression level in the immunoblot (top) and NHEJ efficiency (bottom). Mean ± S.D. from triplicate measurements. (D) Rescue of NHEJ in siASF1a-transfected 293B cells by expression of siRNA-resistant ASF1a. Empty (+EV) or ASF1a expressing vector resistant to siASF1a (+ASF1a) was co-transfected with HA-I-SceI. Immunoblots (top) and quantitation of NHEJ efficiency (bottom). Mean ± S.D. of triplicates. (E) Depletion of ASF1a renders cells sensitive to ionizing radiation (IR). Cell viability was quantified and presented as mean ± S.D. from triplicate measurements (lower panel). Representative images (upper panel). (F) Dose-dependent sensitivity to bleomycin of ASF1a depleted cells. The indicated dose of bleomycin was treated for 24 hr after 48 hr from first siRNA transfection. Mean ± S.D. from triplicates.
