Figure 5. ASF1a interacts with MDC1, and the FHA domain of MDC1 is required for ASF1a localization to DSBs.
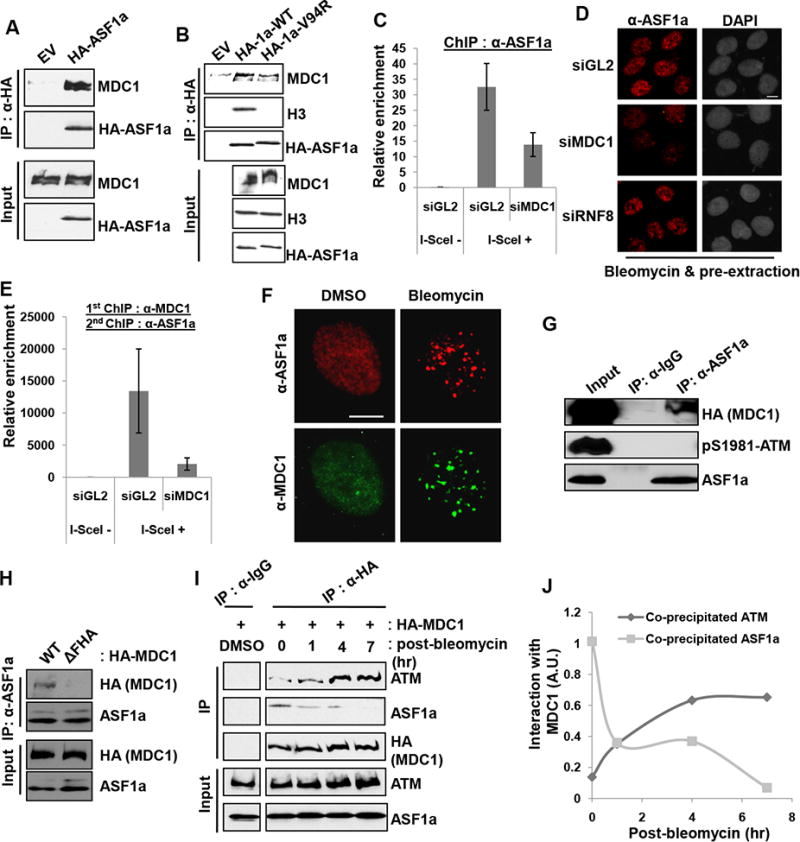
(A) HA-ASF1a precipitates contain endogenous MDC1. Immunoblots of immunoprecipitates or input lysate. (B) Histone binding by ASF1a not required for the interaction with MDC1. Wild-type or Val94Arg mutant of HA-ASF1a was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody. (C) MDC1 is required for ASF1a localization at I-SceI cut site. ChIP assay was performed as described in the METHOD DETAILS. (D) MDC1 dependent association of ASF1a with chromatin after DNA damage. U2OS cells treated with bleomycin for 1 hr followed by pre-extraction, to remove soluble proteins, were fixed and immunostained. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Co-localization of MDC1 and ASF1a to I-SceI cut site. The eluate from anti-MDC1 ChIP was applied to an anti-ASF1a ChIP. (F) Co-localization of ASF1a- and MDC1-foci at DSBs. (G) Untagged ASF1a co-immunoprecipitates MDC1 but not phospho-ATM. (H) ASF1a-MDC1 interaction needs the FHA domain of MDC1. HA-MDC1 wild type or FHA deletion mutant (∆55-124 a.a.) was overexpressed in HEK293T cells followed by bleomycin treatment for 14 hr. (I and J) MDC1 interaction with ASF1a decreases as its interaction with ATM increases after DNA damage. The immunoblots with indicated antibodies (I) and quantification of co-precipitated ATM or ASF1a with HA-MDC1 after pulse-treatment of bleomycin (J).
