Figure 5.
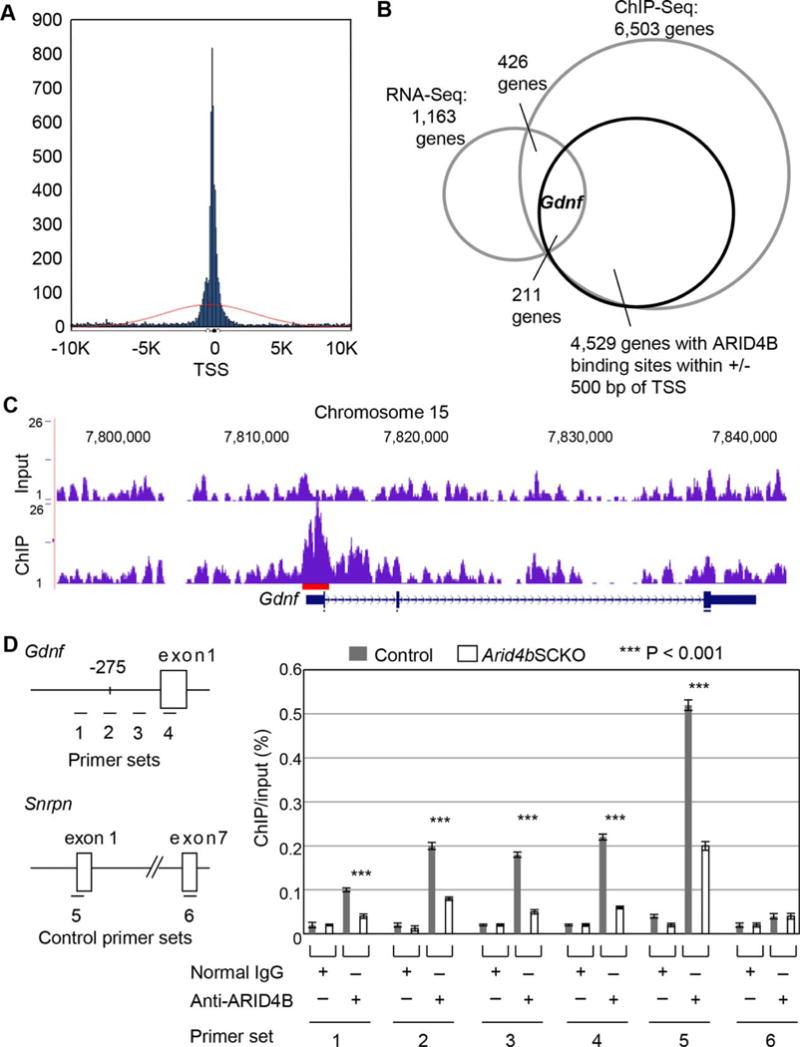
Identification of Gdnf as an ARID4B direct target in the neonatal testes. (A): Histogram of ARID4B binding sites within ± 10 Kb ranges of transcriptional start sites (TSS) of target genes identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-Seq analysis. Results of ChIP-Seq analysis using anti-ARID4B antibody (blue peaks) and input (red line) showed enrichment of ARID4B binding close to the TSS of genes. (B): RNA-Seq and ChIP-Seq analyses identified Gdnf as one of the potential ARID4B direct targets with ARID4B binding sites within ± 500 bp of the transcriptional start sites. (C): ChIP-Seq analysis showed the enrichment of ARID4B binding to the promoter region of Gdnf. Results were analyzed using the mouse mm10 assembly on UCSC genome browser. Red line indicates the ARID4B binding region (D): ChIP-qPCR analysis showed that ARID4B was recruited to the Gdnf promoter. Cross-linked chromatin from testes of the control and Arid4bSCKO mice at P1.5 was immunoprecipitated with normal rabbit IgG or anti-ARID4B antibody. Immunoprecipitated DNA was subject to qPCR analysis using the primer sets 1–6. The promoter region of Gdnf is shown with four primer sets 1–4, which indicate the region of each qPCR product in ChIP-qPCR analysis. The distance (bp) upstream of −275 that indicates from the transcriptional start site of Gdnf is the starting point of the ARID4B binding region identified by ChIP-Seq analysis. The primer set 5 that overlaps the Snrpn exon 1 was used as a positive control, and the primer set 6 that overlaps the Snrpn exon 7 was used as a negative control. Data are means ± SEM. Abbreviations: ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; TSS, transcriptional start site.
