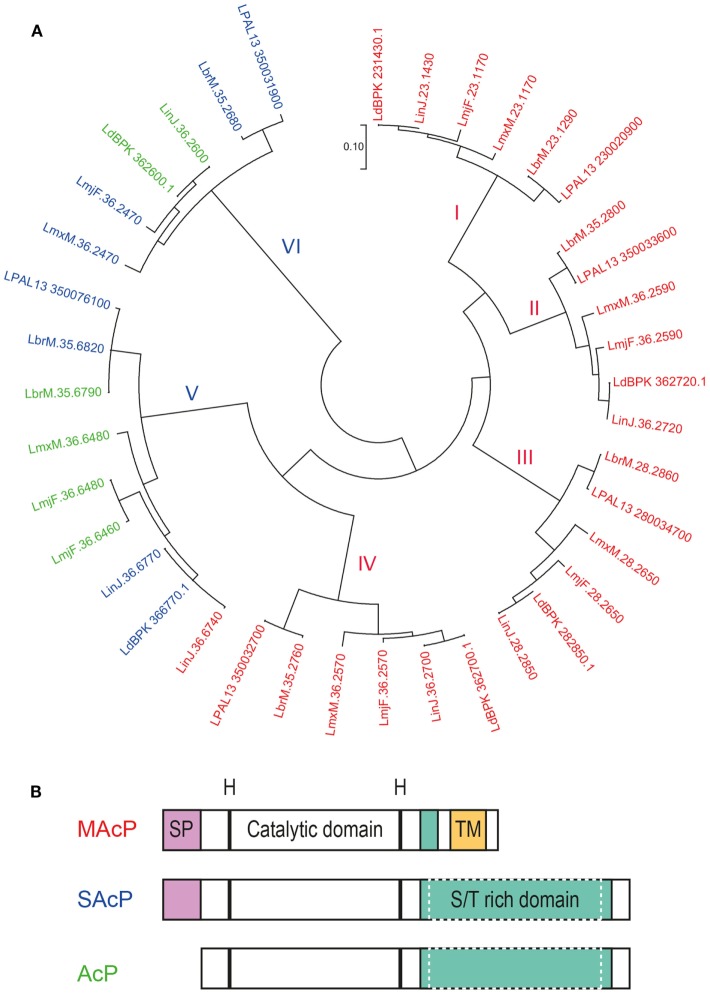
Figure 4.
Acid phosphatases (AcPs) of Leishmania parasites. AcP, secreted by Leishmania parasites or expressed on their surface, belong to the family of histidine phosphatases. (A) Phylogenetic comparison between histidine phosphatases of L. major Friedlin, L. infantum JPCM5, L. donovani BPK282A1, L. mexicana MHOM/GT/2001/U1103, L. braziliensis MHOM/BR/75/M2904, L. panamensis MHOM/COL/81/L13. Available gene sequences were extracted from the TriTrypDB Kinetoplastid Genomics Resource database (IPR: 000560) and were used to construct a phylogenetic topology with the minimum evolution method. The evolutionary distance (scale) is measured in number of base substitutions per site. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Minimum Evolution method (142). The evolutionary distances were computed using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method (143) and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. The minimum evolution tree was searched using the Close-Neighbor-Interchange (CNI) algorithm (144) at a search level of 1. The Neighbor-Joining algorithm (145) was used to generate the initial tree. The analysis involved 39 nucleotide sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There was a total of 409 positions in the final data set. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA7.0.18 (146). Protein sequences of the respective genes were analyzed for the presence of a putative signal peptide (SP) and transmembrane domain (TM) with the Phobius software (147). Genes are labeled in red for the membrane AcP (MAcP) containing a signal peptide (SP) and transmembrane domain (TM), in blue for the secreted AcP (SAcP) containing only a SP and in green for the phosphatases lacking both domains. (B) Schematic organization of the protein domains of Leishmania AcP. Membrane and secreted AcP have a SP at their N-terminus followed by a catalytic domain based on histidine residues. Next, AcP harbor a serine/threonine(S/T)-rich domain that varies in length and can be significantly larger in SAcPs. Finally, MAcPs harbor a TM close to their C-terminus. Some AcPs (green in panel A) are devoid of SP and TM but can harbor long S/T-rich domains.