Figure 1.
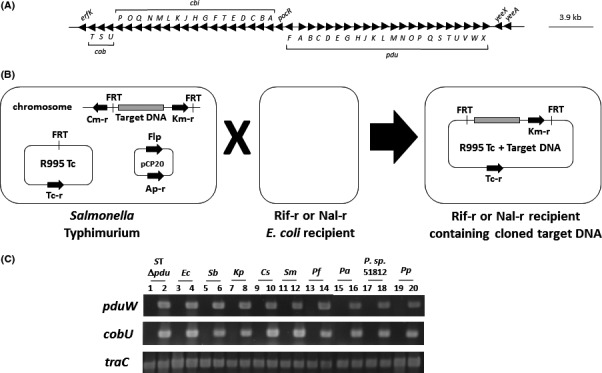
Cloning of the S. Typhimurium pdu and cob/cbi genes using FRT‐Capture. Panel A: A gene map of the targeted S. Typhimurium pdu and cob/cbi genomic segment cloned via FRT‐Capture. Panel B: A schematic diagram of the FRT‐Capture technique (not drawn to scale). FRT sites were inserted into regions flanking the target DNA (i.e. the pdu/cob/cbi region) in S. Typhimurium. Plasmids R995 (containing a single FRT site) and pCP20 (expressing FLP recombinase) were sequentially introduced into this strain. This allows FLP‐mediated excision of the target DNA and insertion into R995. The cloned target DNA construct is isolated upon conjugation to a fresh E. coli recipient strain containing appropriate counterselection (such as Rif‐R or Nal‐R). Panel C: PCR analysis of R995 + pdu ST in a range of Gram‐negative bacterial backgrounds. The pduW and cobU genes are specific for the cloned DNA segment, and the traC gene is present on the R995 vector. PCR products were analysed using 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis followed by staining with SYBR Safe and UV light visualization. Abbreviations: ST Δpdu = Salmonella Typhimurium Δpdu; Ec = Escherichia coli; Sb = Salmonella bongori; Kp = Klebsiella pneumoniae; Cs = Cronobacter sakazakii; Sm = Serratia marcescens; Pf = Pseudomonas fluorescens; Pa = Pseudomonas aeruginosa; P. sp. 51812 = Pseudomonas species 51812; Pp = Pseudomonas putida. Odd numbered lanes are R995‐containing, and even numbered lanes are R995 + pdu ST‐containing.
