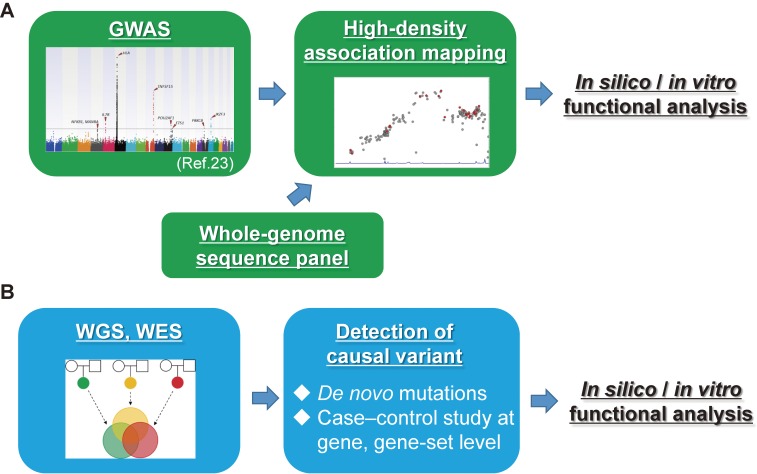
Figure 1.
Flow of screening of the whole-genome for candidate functional disease-causal/susceptible variants. (A) Flow of screening for common disease-susceptible variants. Susceptibility gene loci are detected using GWAS. High-density association mapping is then performed by genotype imputation analysis and is followed by a case–control association study using the data of the GWAS and a whole-genome sequencing panel that is acquired from the general population using NGS. In silico/in vitro functional analyses are needed for the identification of disease-susceptible variants. (B) Flow of screening for rare disease-causal rare variants. All variants are detected by WES and WGS, and candidate disease-causal variants are then identified using large-scale bioinformatics analysis. In silico/in vitro functional analyses are needed for functional evaluation of disease-causal variants.