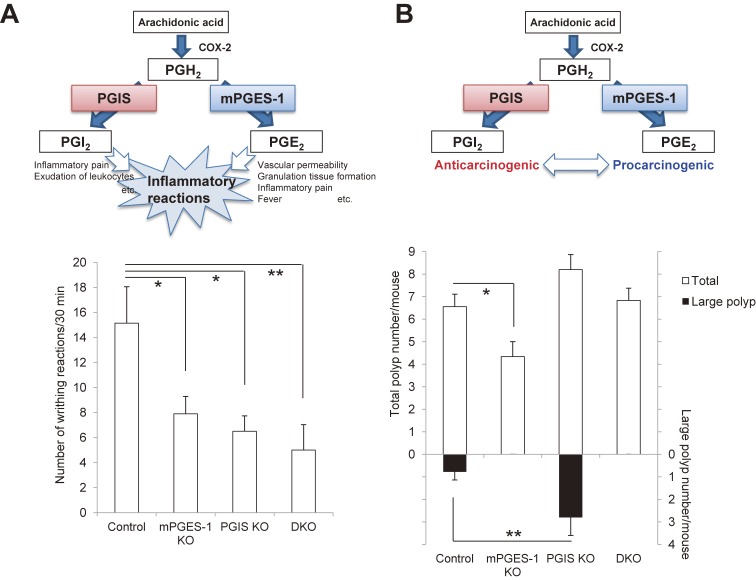
Figure 6.
Crosstalk between PGIS-derived PGI2 and mPGES-1-derived PGE2 in inflammatory reactions (A) and carcinogenesis (B). A: Crosstalk between PGIS and mPGES-1 in inflammatory reactions. Both COX-2/PGIS-derived PGI2 and COX-2/mPGES-1-derived PGE2 function as proinflammatory agents. They cooperatively exacerbate inflammatory reactions. As shown in the lower panel, the LPS-primed acetic acid-induced writhing reaction was reduced in both the PGIS KO and mPGES-1 KO mice, and it was suppressed more effectively in the PGIS/mPGES-1 DKO mice compared with the PGIS KO and mPGES-1 KO mice (*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs control mice).85) B: Crosstalk between PGIS and mPGES-1 in carcinogenesis. COX-2/PGIS-derived PGI2 functions as an anticarcinogenic agent in contrast to COX-2/mPGES-1-derived PGE2 in various tissues. When mPGES-1-derived PGE2 increases and then exceeds the anticarcinogenic actions of PGIS-derived PGI2, a tumor might progress. As shown in the lower panel, in an AOM-induced colon cancer model, mPGES-1 deficiency decreased the number of polyps, whereas PGIS deficiency tended to increase the polyp numbers and significantly increased the number of large polyps (*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs control mice).85)