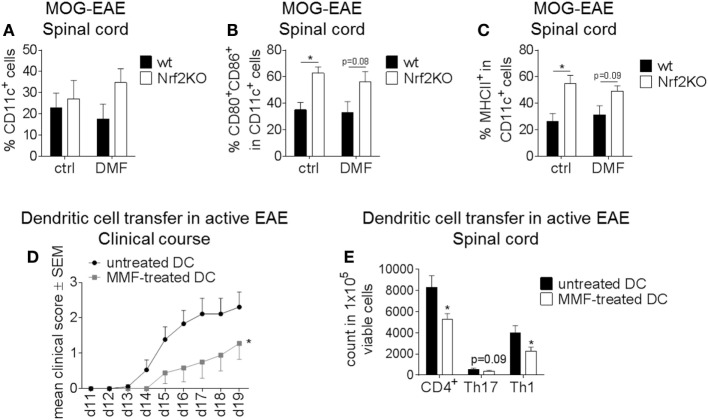
Figure 4.
Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) signaling alters disease course and immune cell activation in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mouse model. (A–C) Ex vivo flow cytometry analysis of CD11c+ cells (A) as well as CD80/CD86 (B) and MHCII (C) expression in the spinal cord under dimethyl fumarate (DMF) versus control treatment on day 14 after active EAE induction (n = 3–4 mice per group, *p < 0.05). (D) Clinical course of MOG35–55 EAE after dendritic cell (DC)-transfer. Untreated or metabolite monomethyl fumarate (MMF) pretreated in vitro cultured bone marrow-derived DC (BMDC) were transferred into EAE mice on days 2 and 7 after MOG immunization. Data are shown on a 5-point score scale (n = 9 mice per group, data pooled from two independent experiments, *p < 0.05). (E) Ex vivo flow cytometry analysis of total CD4+, Th1, and Th17 cells in the spinal cord of DC-transferred mice at the maximum of disease (n = 7–8 mice per group, data pooled from two independent experiments, *p < 0.05).