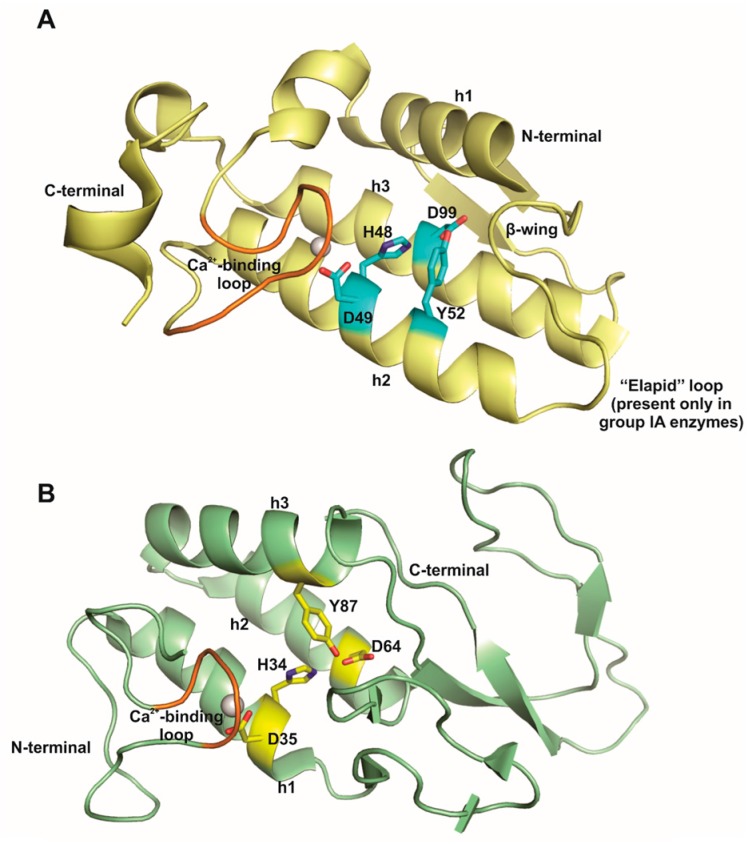
Figure 1.
Cartoon representation of canonical tertiary structure of phospholipases A2 from (A) snake venoms of groups I and II; and, (B) bee venom of group III. The conserved structural motifs are highlighted: α-helices 1, 2, and 3 (h1, h2 and h3, respectively); the β-wing, the flexible C-terminal region, the Ca2+-binding loop (in orange) and the “elapid” loop, an insertion of two or three amino acids in region 52–65 present only in class IA enzymes. The conserved catalytic network formed by a histidine (H), two aspartic acids (D) and a tyrosine (Y) residues are also highlighted in cyan (in snake venom PLA2) and in yellow (in bee venom PLA2) sticks. The figures were generated using the crystal structures of group IA PLA2 from Naja naja venom (PDB ID 1PSH) and of group III PLA2 from Apis mellifera venom (PDB ID 1POC). Modified from Fernandes et al., 2014: Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Preoteins and Proteomics, volume 1844, pages 2265-2276, Elsevier, copyright 2014 [23].