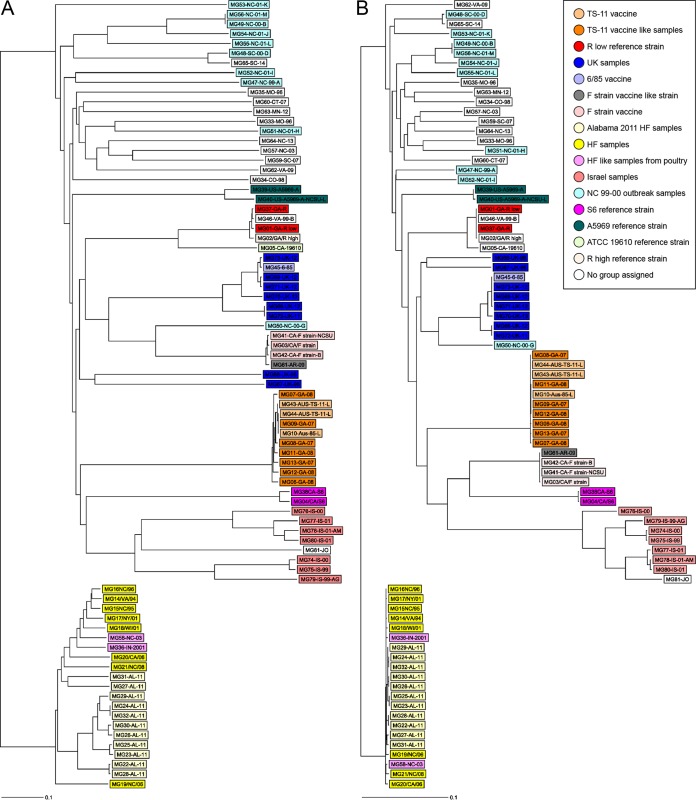
FIG 2.
Side-by-side core genome allele-based and core genome SNP-based rooted neighbor-joining tree for 81 clinical and reference M. gallisepticum samples using SeqSphere+ software. Note the high degree of congruence among the two trees. (A) The neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogenetic tree based on the allelic profiles of 425 single-copy core genome targets from 81 clinical and reference M. gallisepticum samples using SeqSphere+ software. Core genome allelic profiles were determined by loading de novo assemblies into the M. gallisepticum cgMLST scheme developed in this study. The distance matrix was built from all pairwise allelic profile comparisons of 425 cgMLST targets, using the pairwise ignoring-missing-values option in SeqSphere+ software. Using this option, genes with at least one missing value are not completely removed from the comparison but are ignored only during a pairwise comparison in case of a missing value. (B) Core genome SNP-based tree was built based on 5,741 filtered SNP out of 18,823 total SNP. SNP were identified after alignment of the concatenated 324 cgMLST target gene sequences after exclusion of targets with missing values present in all 81 samples, using the tool find single-nucleotide variants in Ridom SeqSphere+ software with the default setting for filtering out InDels and a neighboring SNP filtering window of 10 bases. Groups of samples are color coded according to the key.