Fig. 2.
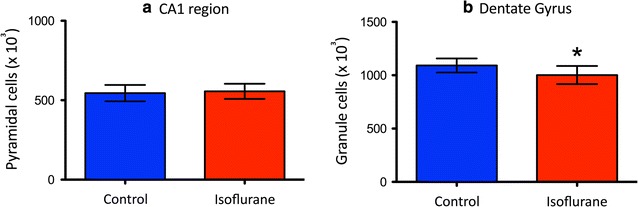
Gestational exposure to isoflurane resulted in region-specific cell loss in the adult hippocampus. No changes were detected in the pyramidal layer of the CA1 area of adult male rats following isoflurane exposure in utero (N = 13) compared to control rats (N = 10) (a). However, isoflurane exposure at E14 (N = 13) was associated with a significant decrease in the number of cells in the granule cell layer of the dentate gyrus (*P = 0.01) compared to control rats (N = 10) (b). Data were analyzed using Student’s t-test and expressed as mean ± S.D
