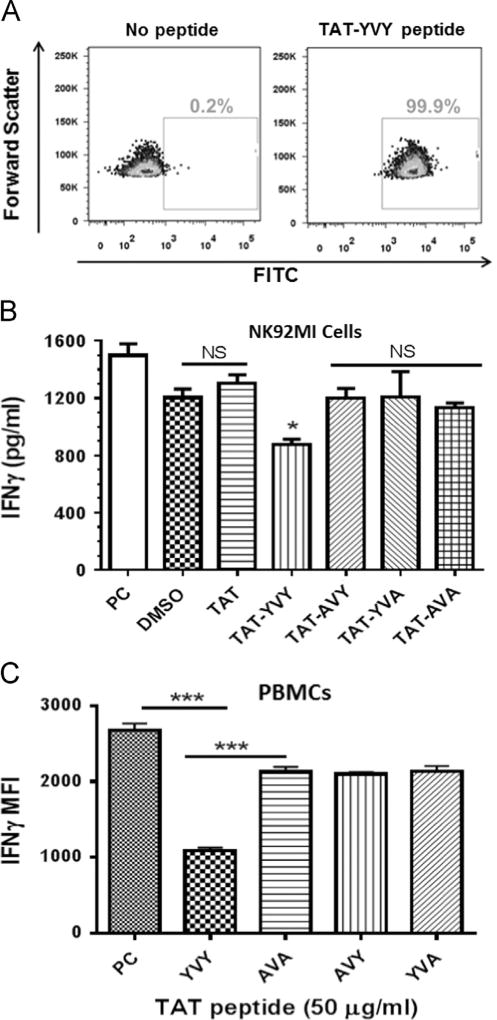
Fig. 8.
Conserved tyrosine residues within HPgV envelope protein (E2) protein were required for inhibition of IL-12 signaling in primary NK cells and NK cell lines. Conserved tyrosine residues within HPgV E2 protein (a.a. 85, 87) predicted to modulate Tyk2 kinase function were predicted to serve as a substrate for Tyk2. NK92MI cells were incubated with no peptide or a FITC-labeled HPgV E2 peptide containing the HIV TAT protein transduction domain (TAT). Peptide uptake is shown by FITC fluorescence (A). NK92MI cells (B) or peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs; C) were incubated with the peptide vehicle (DMSO; PC), TAT peptide, native HPgV peptide with TAT (TAT-YVY) or mutant TAT-HPgV peptides as indicated for 6 h prior to IL12 stimulation (2 ng/ml). Following 18 h incubation, IFNγ was quantified in cell culture supernatant by ELISA (B) or intracellularly gating on CD3−/CD56+ NK cells by flow cytometry (C). Data represent cultures from three healthy, HPgV negative independent blood donors. * = p < 0.01 vs. DMSO and TAT only peptide (T test). *** = p < 0.01 vs. PC.