Figure 1.
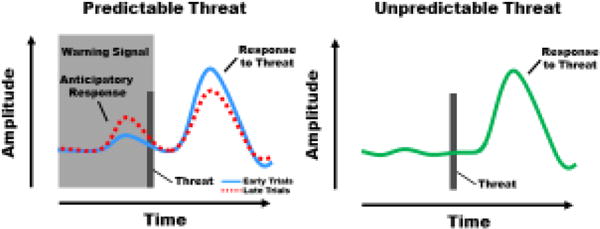
Illustration depicting anticipatory responses and emotional responses to threat during Pavlovian fear conditioning. A) During early conditioning trials (solid line), anticipatory responses to the warning signal are relatively small and the emotional response to the threat is relatively large. During late conditioning trials (dashed line), once the association between the warning signal and threat has formed, the warning signal elicits a relatively large anticipatory response and the predictable threat elicits a relatively small emotional response. Thus, the emotional response to threat is diminished on late compared to early conditioning trials. B) The emotional response to the unpredictable threat is similar to the response to predictable threat during early (solid line in A), but not late (dashed line in A), conditioning trials. Thus, the emotional response is larger for unpredictable (B) than for predictable (dashed line in A) threat.
