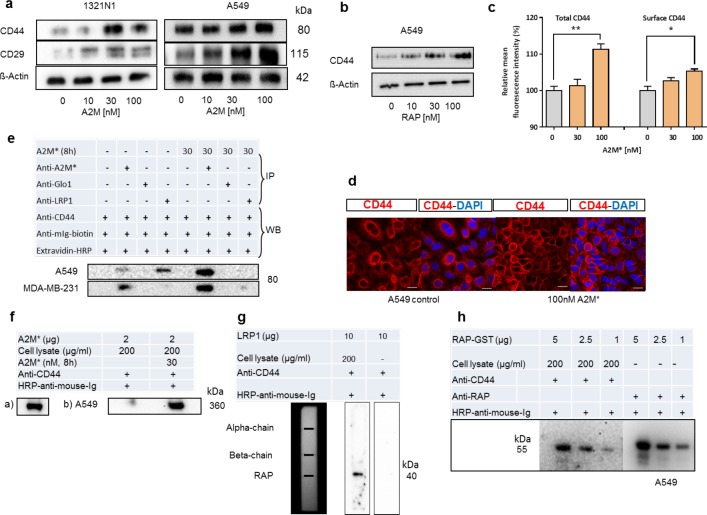
Fig 2. Effect of A2M* on expression of CD44 and CD29 in different tumour cell lines.
(a) 1321N1 and A549 cells were cultured in the absence and presence of increasing concentrations of A2M, lysed and immunoblotted for CD44 and CD29. (b) A549 cells were stimulated by RAP and treated as shown in (a). (c) A549 cells were treated with A2M* and expression of total and cell surface CD44 was analysed by flow cytometry (n = 3), error bars mean ± sem, t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (d) A549 cell were treated with 100 nM A2M* for 12h, fixed by paraformaldehyde and immunestained for CD44 and counterstained with DAPI. (e) Immunoprecipitation of CD44 in A2M*-stimulated and non-stimulated A549 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Cells were treated with 30 nM A2M* for 24h, lysates were precipitated with different antibodies (anti-LRP1, anti-A2M*, anti-GLO1) and Western blotted for CD44 protein. (f) Ligand blot of A2M* for CD44 binding. A2M* was blotted to membranes which were incubated with cell lysate of A549 afore stimulated by 30 nM A2M* for 8h. Binding of CD44 to immobilized A2M* was detected by anti-CD44/HRP-anti-mouse-Ig. a) Immobilized A2M* detected by anti-A2M*/HRP-anti-mouse-Ig and b) Detection of binding of CD44 to immobilized A2M*. (g) Ligand blot demonstrating binding of CD44 to LRP1-associated RAP. Membrane-blotted LRP1 was incubated with A549 cell lysate and bound CD44 was detected by respective antibodies. (h) Recombinant RAP was electro-blotted, followed by incubation with A549 cell lysate. Detection of CD44 bound to immobilized RAP was accomplished by anti-CD44/HRP-anti-mouse-Ig. Immobilized RAP was detected by anti-RAP antibody (blotting control).