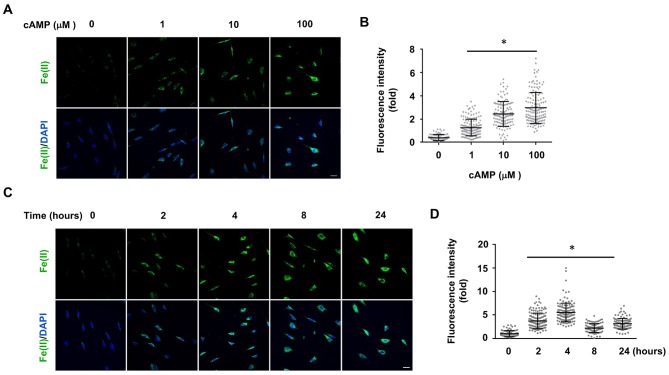
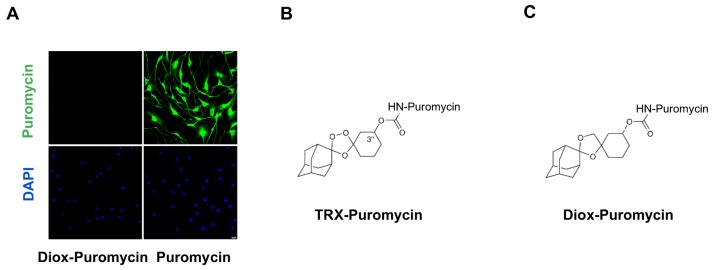
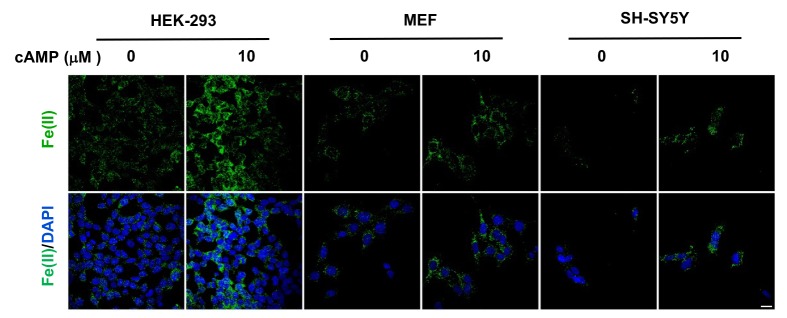
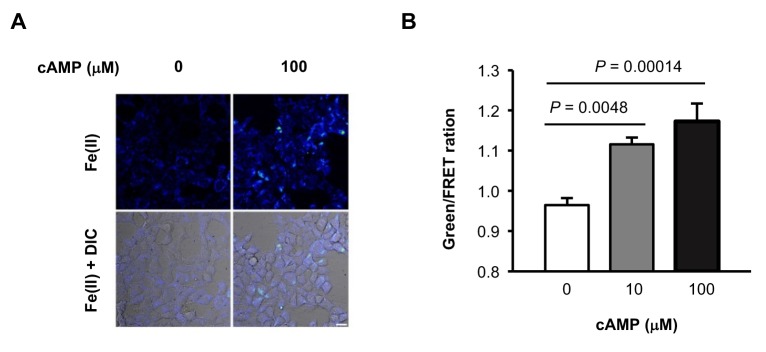
Figure 2. cAMP increases the intracellular labile Fe(II) pool in cells.
(A) cAMP (1–100 μM) treatment for 4 hr increased the intracellular labile Fe(II) pool detected by Trx-Puro ferrous iron probes. (B) IF quantification shows the dose-dependent effect of cAMP on labile Fe(II). (C) cAMP (100 μM) treatment for 2–24 hr increased labile Fe(II). (D) IF quantification shows the peak effect of cAMP on labile Fe(II) after treatment for 4 hr. Scale bar = 20 μm. *p<0.0005 (n = 3 independent experiments with three biological replicates in each group, error bars denote standard deviation).