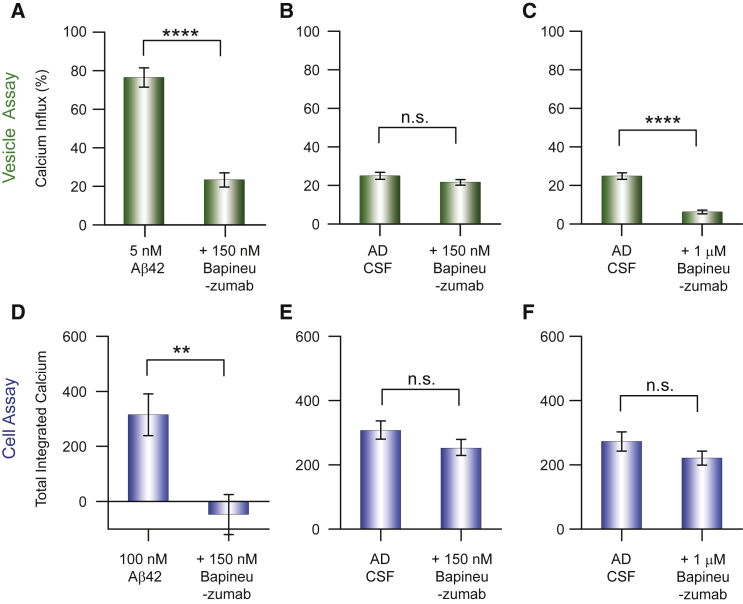
Figure 3.
Assessing the Ability of the Antibody Bapineuzumab to Reduce the Ca2+ Influx Resulting from the Addition of Aliquots of Human CSF
(A and B) Inhibition of the influx of Ca2+ ions into individual vesicles caused by aggregates of recombinant Aβ42 (A) or resulting from the addition of aliquots of AD CSF by bapineuzumab (150 nM) (B).
(C) The inhibition of the influx of Ca2+ ions into individual vesicles resulting from the addition of aliquots of CSF by a high concentration of the antibody bapineuzumab (1 μM).
(D and E) Inhibition of the Ca2+ influx into astrocytes caused by aggregates of synthetic Aβ42 (D) or resulting from the addition of aliquots of human CSF by the antibody bapineuzumab (150 nM) (E).
(F) The inhibition of the Ca2+ influx resulting from the addition of aliquots of human CSF into astrocytes by a high concentration of bapineuzumab (1 μM). The statistical data for these experiments are summarized in Tables S1 and S2. Error bars, SEM.