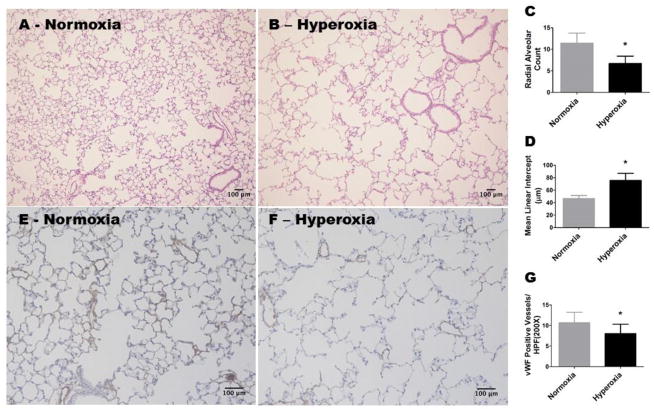
Figure 1. Alveolar and pulmonary vascular development continues to be interrupted in adult mice exposed to hyperoxia during the neonatal period.
WT mice were exposed to either 21 % O2 (normoxia) for 8 weeks, or 70 % O2 (hyperoxia) for 2 weeks followed by normoxia for 6 weeks (n = 6 mice/group). A and B: Representative hematoxylin and eosin-stained lung sections (100x magnification). C: Radial alveolar counts. D: Mean linear intercepts. E and F: Representative von Willebrand Factor (vWF)-stained lung blood vessels (200x magnification). G: Quantitative analysis of vWF-stained lung blood vessels per high power field (HPF). Values are presented as the mean ± SD. Significant differences between normoxia- and hyperoxia-exposed mice are indicated by *, p < 0.05 (t-test). Scale bar = 100 μM.