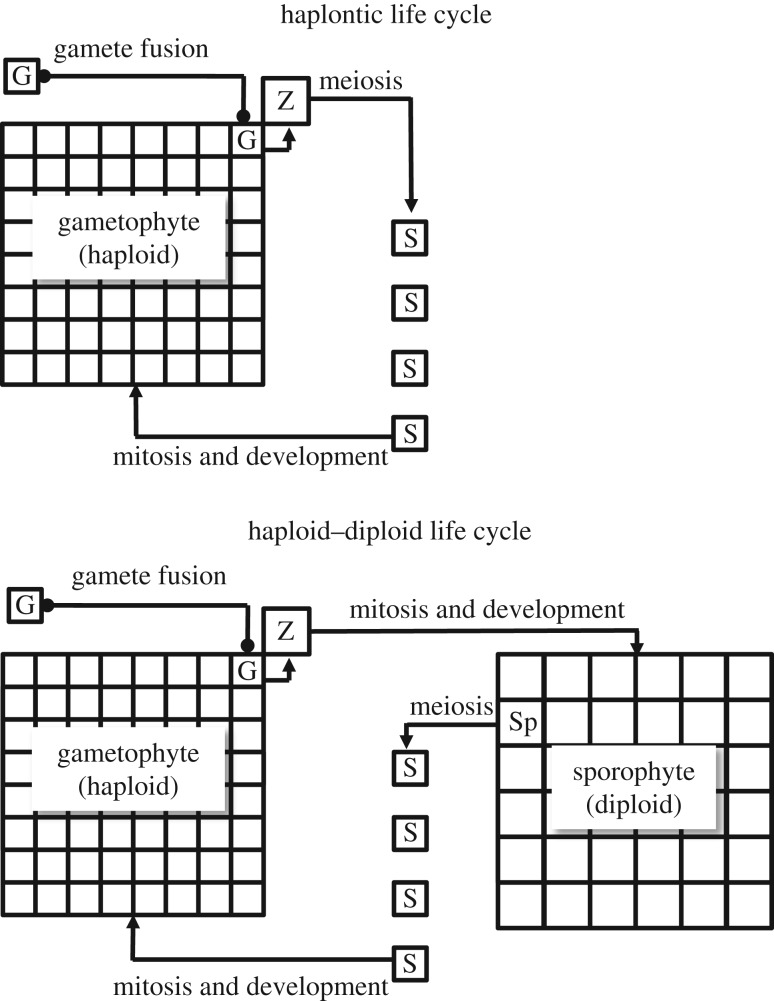
Figure 1.
Diagrammatic representation of haplontic and haploid–diploid life cycles. In these examples gamete (G) fusion takes place on the gametophyte, which retains the ensuing zygote (Z). Haplontic: zygotic meiosis gives rise directly to zoospores (S). Haploid–diploid: zygote undergoes mitosis and development. Spores (S) develop from spore mother cells (Sp) on the sporophyte. In bryophytes the sporophyte is matrotrophic (i.e. retained on and nurtured by the gametophyte). In basal vascular plants, gametophyte and sporophyte are separate, free-living organisms.