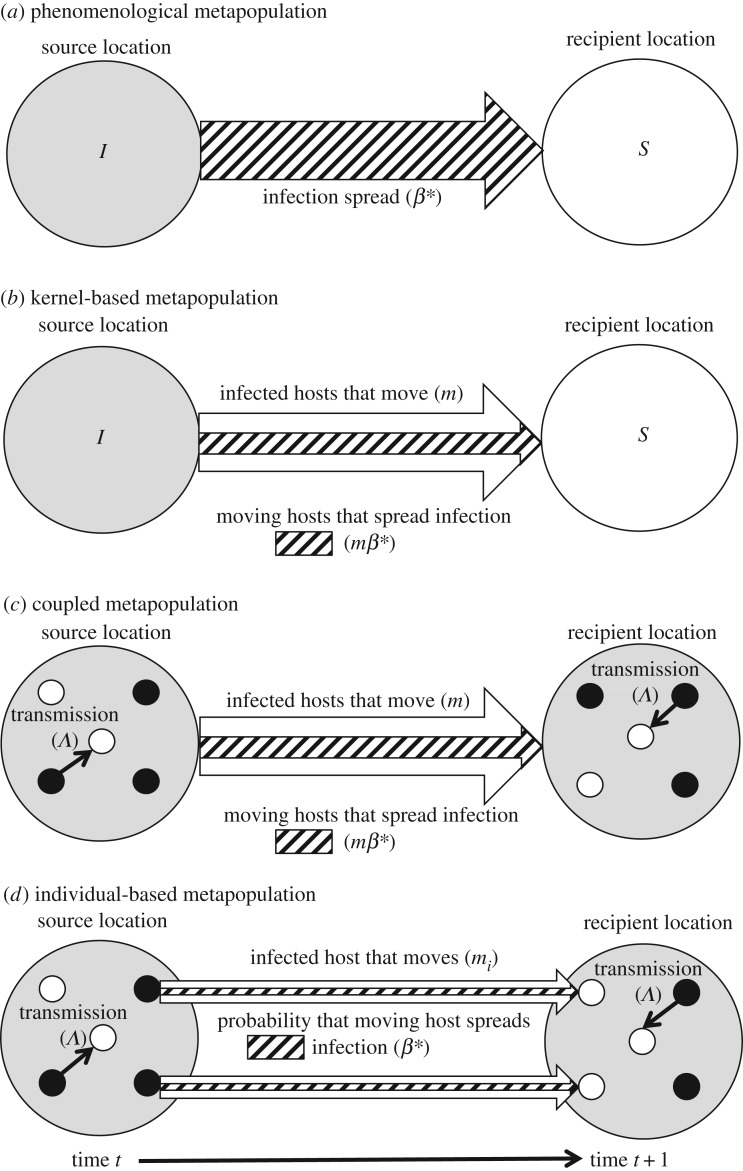
Figure 1.
Metapopulation-based spatial disease models track locations of hosts and either (a) simulate infection spread based on connectivity measures without explicitly considering host movement or (b) define proportion of hosts that change locations between time steps (white arrow) with infection spread occurring from a proportion of hosts that change from infected locations to susceptible locations (striped arrow). (c) Coupled metapopulation models link local processes such as transmission (thin black arrow) to the between-location processes of host movement and infection spread. (d) Individual-based network models track movements of each host (denoted by subscripts i,j).