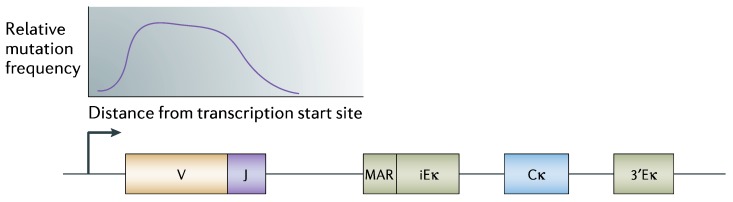
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of gene-specific targeted hyper-mutation in immunoglobulin gene loci. The mutation rate is greatly increased only in the variable part of the genome, which is a ~1.5 kilobase region in each of the three immunoglobulin loci. In this figure, the rectangular elements (V, J, MAR, iEκ, Cκ, 3′Eκ) represent different functional parts of the DNA sequence for the immunoglobulin protein. V is the variable part, subject to hypermutation, while the other parts are fixed. For further details on the functions of the parts see Odegard and Schatz [22]. Those details are not important for the purposes of this article.