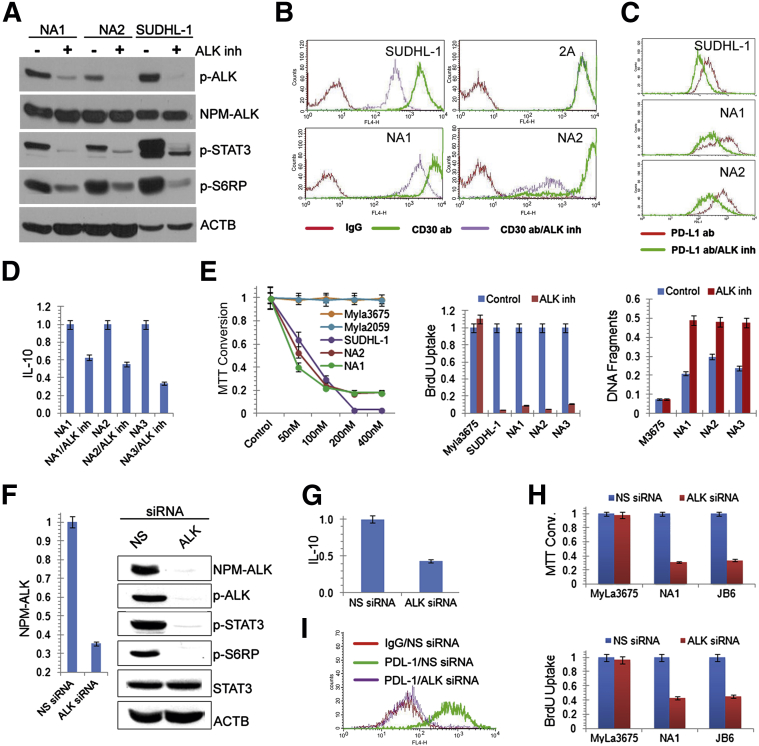
Figure 3.
NPM-ALK–dependence of the transformed CD4+ T cells. A–D: Suppressive effect of the ALK inhibitor CEP-28122 (100 nmol/L) on phosphorylation of the cell-signaling proteins ALK, STAT3, and S6RP in NA1, NA2, and control SUDHL-1 cells (A); expression of CD30, with CD30-ALK− T-cell line 2A serving as a negative control (B); expression of PD-L1 (C); and synthesis of IL-10 (D). E: Effects of ALK inactivation by CEP-28122 on cell growth (left panel), cell proliferation (middle panel), and cell apoptotic rate (right panel). ALK− T-cell lines MyLa2059 and MyLa3675 and ALK+ ALCL cell line SUDHL-1 served as controls. F–I: Depletion of NPM-ALK mediated by ALK siRNA and its effect on phosphorylation of the cell-signaling proteins STAT3 and S6RP (F), IL-10 expression (G), cell growth (H), and PD-L1 expression (I). Nonspecific (NS) siRNA was used as a negative control (F–I). BrdU, bromodeoxyuridine.