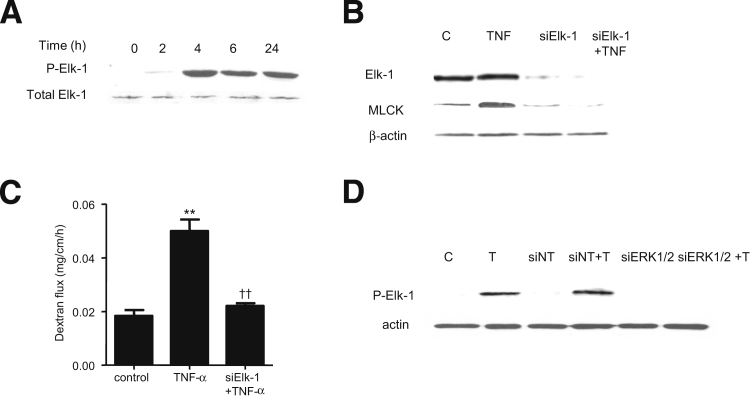
Figure 11.
A: TNF-α causes a time-dependent increase in Elk-1 phosphorylation; total ERK1/2 was used for equal protein loading. B: Elk-1 siRNA transfection results in a near-complete depletion of mouse intestinal Elk-1 protein expression and prevents the TNF-α–induced increase in mouse intestinal MLCK protein expression. C: Elk-1 silencing inhibits the TNF-α–induced increase in mucosal-to-serosal flux of dextran 10K. D: siRNA-induced knockdown of ERK1/2 prevents TNF-α–induced phosphorylation of Elk-1 in mouse intestinal tissue. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 3. Experimental period, 24 hours (B and C); 4 hours (D). ∗∗P < 0.0001 versus control. ††P < 0.0001 versus TNF-α treatment.